The Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI) sector in India have witnessed exponential growth in recent years, driven by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and an evolving customer landscape. However, this rapid evolution has brought about its own set of challenges, particularly in the realm of talent acquisition and management. In this article, we will explore the key talent challenges faced by BFSI companies in India and examine how some industry players are addressing these issues effectively.
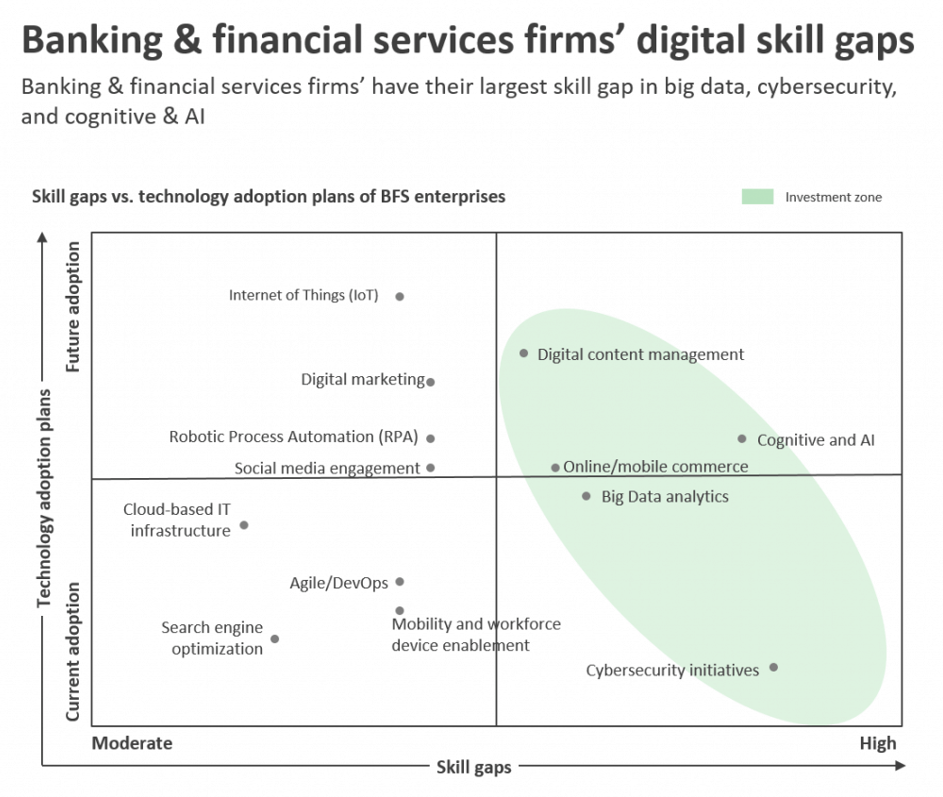
Skill Shortages and Technological Advancements: One of the foremost challenges faced by the BFSI sector in India is the ever-growing gap between the skills demanded by the industry and the skills possessed by the available talent pool. With the rapid integration of technologies like artificial intelligence, blockchain, and data analytics into banking and financial services, there is a pressing need for professionals with expertise in these domains.
Example: HDFC Bank’s Future Bankers Program: HDFC Bank, one of India’s leading private sector banks, has taken a proactive approach to address skill shortages. The bank launched the Future Bankers Program, an initiative designed to identify and groom young talents for roles in technology and banking operations. The program focuses on developing skills in areas such as data analytics, machine learning, and digital banking to ensure a steady supply of talent equipped with the necessary competencies.
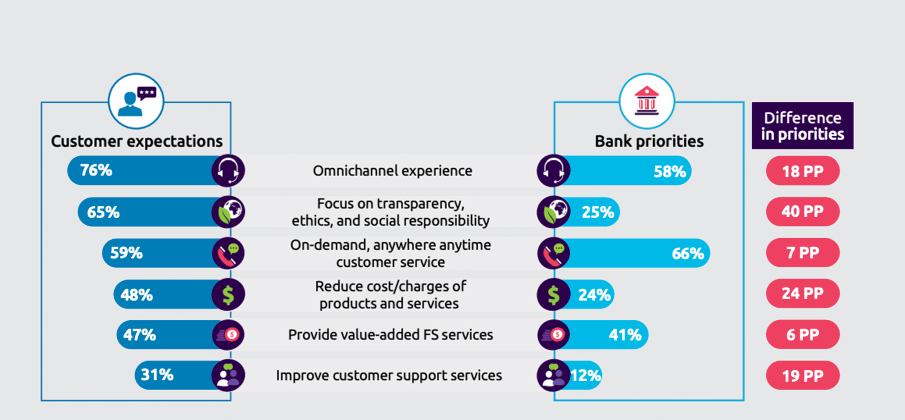
Changing Customer Expectations: As customers become more digitally savvy, their expectations from BFSI services are evolving. This shift is prompting companies to seek professionals who not only understand traditional banking and finance but also possess a deep understanding of user experience, digital interfaces, and innovative service delivery model.
Example: ICICI Bank’s Digital Village Adoption Program ICICI Bank, a prominent player in the Indian banking sector, has recognized the need for professionals who can bridge the gap between traditional banking and digital innovation. The bank has initiated the Digital Village Adoption Program, wherein it collaborates with local communities to promote digital literacy and financial inclusion. This program not only serves as a community outreach effort but also helps in identifying and nurturing talents with a nuanced understanding of digital banking needs.
Regulatory Compliance and Talent Management: The BFSI sector in India operates in a highly regulated environment, with frequent changes in compliance and governance standards. Keeping abreast of these changes and ensuring that employees are well-versed in compliance measures poses a significant challenges.

Example: Axis Bank’s Compliance Training Initiatives – Axis Bank, a major private sector bank, has invested in comprehensive compliance training programs to equip its employees with the knowledge and skills needed to navigate the intricate regulatory landscape. The bank conducts regular training sessions, workshops, and online courses to keep its workforce updated on the latest compliance requirements. This proactive approach not only ensures regulatory adherence but also fosters a culture of continuous learning within the organization.
Retention of Specialized Talent: The BFSI sector often faces the issue of retaining specialized talent, especially in niche areas such as risk management, fraud detection, and cybersecurity. The demand for experts in these fields is high, and retaining such talent becomes crucial for ensuring the stability and security of financial institutions.

Example: State Bank of India’s Talent Retention Programs– The State Bank of India (SBI), the country’s largest public sector bank, has implemented targeted talent retention programs for employees in critical roles. Recognizing the importance of cybersecurity in the digital age, SBI offers specialized training, career growth opportunities, and competitive compensation packages to retain top-notch cybersecurity professionals. This approach not only helps in talent retention but also enhances the bank’s overall security posture.
Diversity and Inclusion: Achieving diversity and inclusion in the BFSI sector remains a persistent challenge. The industry has historically been male-dominated, and efforts to promote diversity, especially in leadership roles, require intentional and sustained initiatives.
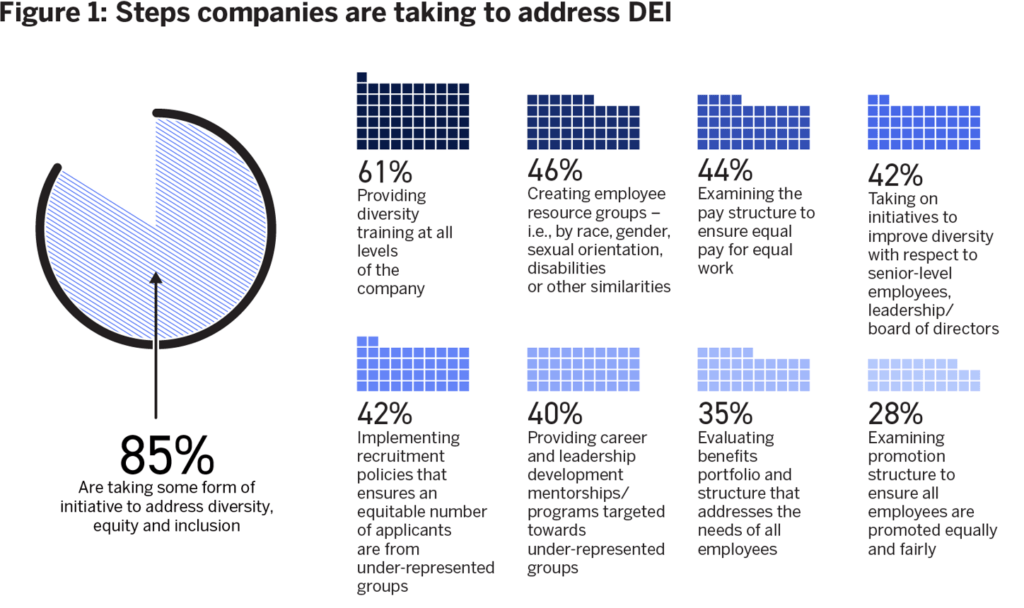
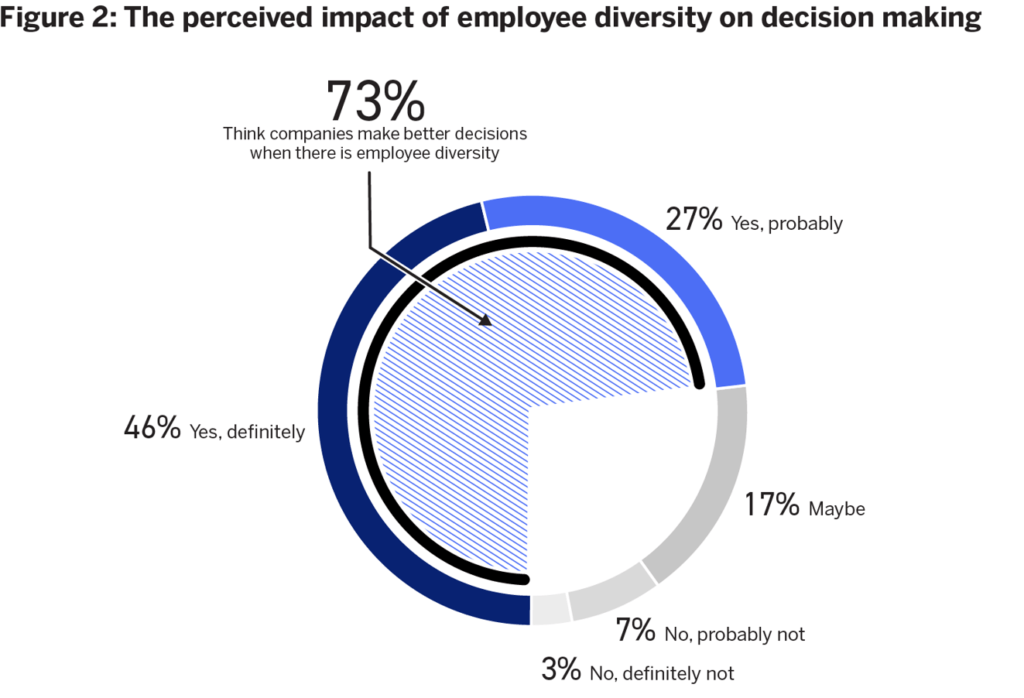
Example: Kotak Mahindra Bank’s Women in Leadership Program– Kotak Mahindra Bank has taken notable steps towards fostering diversity and inclusion within its workforce. The bank’s Women in Leadership Program aims to identify, mentor, and promote talented women professionals into leadership positions. By actively addressing gender disparities, Kotak Mahindra Bank not only contributes to a more inclusive work environment but also benefits from a diverse range of perspectives and ideas.
Conclusion:
The BFSI sector in India is undergoing a transformative phase, marked by technological disruptions, changing customer expectations, and evolving regulatory landscapes. Navigating these changes necessitates a skilled and adaptable workforce. Companies in the sector are responding to talent challenges with innovative programs, strategic partnerships, and a commitment to continuous learning and development. As the industry continues to evolve, the ability to attract, nurture, and retain top talent will remain a critical determinant of success for BFSI companies in India.











