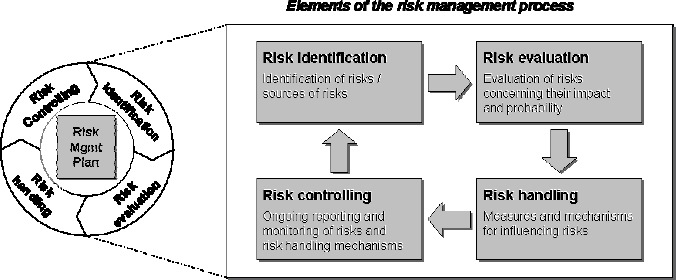
As organizations evolve and face an ever-changing landscape, the integration of risk management principles becomes crucial, extending beyond traditional project management. The Nokia Siemens Networks Risk Management Framework provides a structured approach that goes beyond mere risk identification, offering comprehensive guidelines and tools. This article explores how Human Resources (HR) professionals can leverage this framework to navigate challenges in recruitment, talent management, and overall organizational dynamics.
Utilizing the Framework in HR Scenarios:
Continuous Risk Identification in Talent Acquisition:
- The framework’s risk register proves invaluable in tracking potential risks and issues throughout the recruitment process. HR can maintain a real-time repository of identified risks, such as candidate unavailability, skill gaps, or changes in market demand.
- The risk checklist offers a structured approach to identifying risks at various stages of the recruitment life cycle, ensuring that no significant potential risks are overlooked.
Risk Analysis in Employee Engagement:
- The probability-impact matrix aids HR in analyzing the qualitative and quantitative impact of risks on employee engagement. This allows for a strategic approach to address factors like burnout, communication breakdowns, or inadequate recognition.
- Utilizing risk exposure calculations, HR can prioritize and address risks that pose the most significant threat to employee engagement.
Succession Planning with Risk Response Planning:
- HR can employ the risk response planning guidelines to formulate action plans for potential gaps in succession planning. This involves clearly defined steps, responsible parties, and timelines to reduce the impact of identified risks.
- The risk trigger documentation ensures early detection of issues in succession planning, enabling proactive measures.
Organizational Change Management with Risk Monitoring:
- HR can integrate risk monitoring and control into the change management process. Regular risk reviews, as recommended by the framework, enable HR to assess the effectiveness of change initiatives and make necessary adjustments.
- The risk threshold concept assists HR in prioritizing efforts based on the criticality of risks associated with organizational change.
Risk Analysis and Classification in HR:
Probability and Impact Analysis:
- HR can adopt the framework’s probability-impact matrix to assess the likelihood and severity of risks associated with various HR initiatives. For instance, the impact classification guideline can be applied to employee engagement or talent acquisition risks.
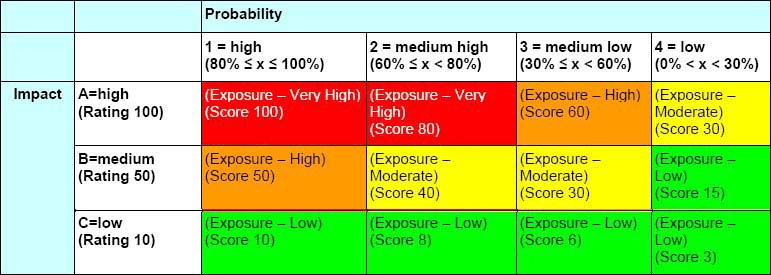
Figure: Impact Probability Matrix
Risk Exposure Calculation:
- The framework’s risk exposure calculation, utilizing the impact-probability matrix, enables HR to quantify and prioritize risks efficiently. This assists in determining the urgency of risk response planning and reporting levels.
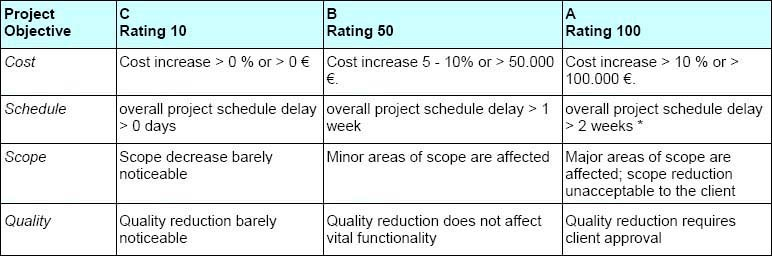
Figure: Impact Classification Guideline
The score indicates the minimum thresholds for categorizing risks under typical conditions. An elevation of the score to the subsequent level, or even the next level beyond, becomes imperative when the risk is influenced by critical factors, including:
- The significance of the particular customer/client
- The project’s crucial role in advancing the relationship with the customer/client
- The risk is already a focal point for the customer/client
- The existence of explicit penalties outlined in the customer/client contract for deviations from project targets.
Risk Occurrence Timeframe:
- HR can categorize risks based on the timeframe in which they may impact HR initiatives. This aids in planning and implementing timely interventions, aligning with the organization’s strategic goals.
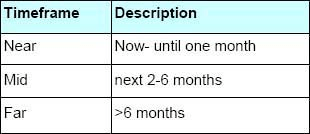
Example: Risk Occurrence Timeframe
Risk Response Planning in HR:
- Actionable Response Plans:
- HR can develop detailed risk response plans, outlining steps to eliminate or mitigate identified risks. These plans should be integrated into the overall HR strategy, impacting time and costs as necessary.
- For each identified risk, a comprehensive risk response must be recorded in the risk register, and agreement with stakeholders should be ensured, overseen by the project manager.
- The objectives of risk response plans include:
- Eliminating the identified risk.
- Reducing the likelihood of the risk occurring.
- Mitigating the impact of the risk on the project objectives.
- Given that risk response plans typically influence both time and costs, it is imperative to calculate the time and cost associated with the defined response plan as accurately as possible. This precision aids in the selection of the most suitable response plan from available alternatives and ensures a thorough examination of whether the response plan is more costly or has a more significant impact on project objectives than the risk itself.
- Upon the successful implementation of a set of response plans, discussions with stakeholders can result in the reassessment and potential reduction of the risk score.
- Ownership and Monitoring:
- Designating a risk owner within the HR team ensures accountability for monitoring risk triggers and implementing response plans. Regular risk reviews become a part of HR meetings, enhancing the adaptability of HR strategies.
Risk Monitoring and Control in HR:
- Continuous Improvement:
- HR can adopt a continuous improvement mindset by utilizing risk efficiency measurement metrics during project closure. This involves assessing the effectiveness of risk analysis and management, driving lessons learned for future HR initiatives.
- Risk Audits in HR:
- Periodic risk audits, as suggested by the framework, enable HR to enhance the maturity and effectiveness of risk management. This includes evaluating the identification, analysis, and mitigation of risks in HR processes.
- A risk audit is an impartial evaluation by domain or technical experts aimed at enhancing the maturity and effectiveness of risk management within the organization. This assessment encompasses:
- Evaluation of the organization’s proficiency in identifying risks.
- Examination of the comprehensiveness and detail of identified risks.
- Assessment of the effectiveness of mitigation or contingency plans.
- Establishment of connections between project-specific risks and broader organizational risks.
- This audit is not a mere evaluation of process adherence but serves as a tool to improve the quality of risk identification and analysis. It provides a platform to benchmark and identify best practices in risk management across diverse projects within the organization.
- Conducted by a group of independent experts through document reviews and interviews, the key outcomes of a risk audit include:
- A tailored checklist for assessing project risks.
- Identification of critical areas for risk analysis within a project (risk taxonomy).
- A risk radar highlighting areas prone to risks within the product group.
- Discovery of additional potential risks based on the audit.
- Identification of the top 10 risks across the organization from key projects, warranting management attention.
Conclusion:
Integrating the Nokia Siemens Networks Risk Management Framework into HR practices elevates the strategic role of HR professionals within an organization. By embracing a systematic approach to risk identification, analysis, and response planning, HR can enhance decision-making processes, improve adaptability to change, and contribute significantly to the achievement of organizational objectives. As risks continue to evolve, the framework provides HR with the tools needed to navigate uncertainties and drive sustainable success.