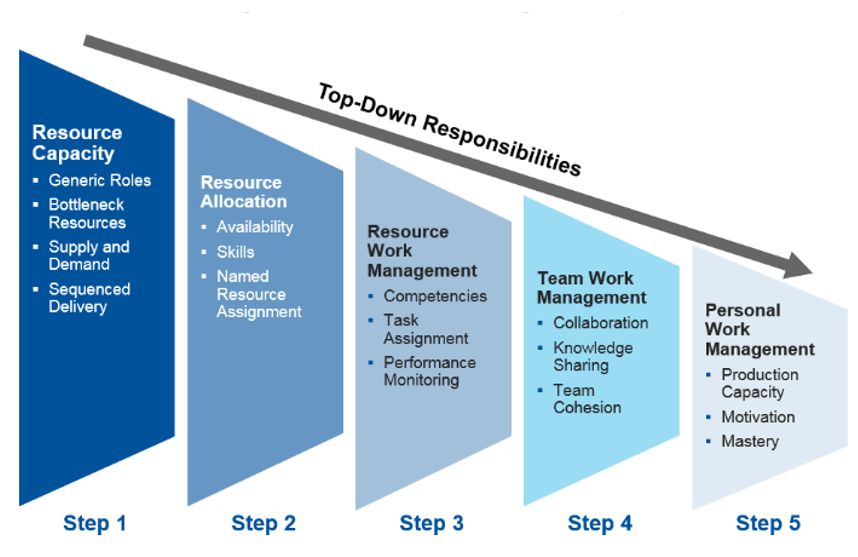
In the dynamic landscape of project management, the effective allocation and management of resources can make or break the success of a project. At the heart of this critical function lies the role of Human Resources (HR) professionals as Project Resource Managers (PRMs). This article delves into the impactful contributions of HRs in project resource management, drawing inspiration from real-life examples where PRMs played a pivotal role in driving successful projects.
Project resource management involves identifying, acquiring, and utilizing resources such as personnel, finances, materials, and technology to achieve project objectives. Effective resource management ensures that the right resources are allocated to the right tasks at the right time. This optimization is vital for project success, as mismanagement of resources can lead to delays, cost overruns, and overall project failure.
The Role of HR in Project Resource Management
- Talent Acquisition and Allocation: HR professionals excel in talent acquisition and management. They can identify the right skills needed for a project and recruit or allocate the appropriate personnel. This includes assessing team members’ strengths, weaknesses, and expertise to ensure a balanced and capable project team.
- Team Building and Collaboration: Successful projects require a cohesive team that can collaborate effectively. HRs are skilled in fostering a positive team culture, resolving conflicts, and promoting effective communication. By building a strong project team, HRs contribute to a harmonious work environment that enhances productivity and project success.
- Skill Development and Training: HRs play a vital role in identifying skill gaps within the project team and facilitating training programs to bridge those gaps. This ensures that team members are equipped with the necessary skills to meet project requirements. Continuous skill development enhances the overall competency of the project team.
- Resource Forecasting: HR professionals can contribute to resource management by forecasting future talent needs. By analyzing historical project data, understanding industry trends, and staying informed about emerging skills, HRs can predict the type and quantity of resources required for upcoming projects.
- Performance Management: HRs are adept at performance management, which involves evaluating and appraising team members’ contributions. By providing constructive feedback and recognizing achievements, HRs motivate team members to perform at their best, contributing to the overall success of the project.
How HRs Can Excel as Project Resource Managers?
- Develop Project Management Skills: HRs interested in excelling as Project Resource Managers should acquire basic project management skills. Understanding project methodologies, timelines, and deliverables will enhance their ability to contribute effectively to resource management.
- Embrace Technology: Project management tools and software can significantly aid in resource allocation and tracking. HRs should familiarize themselves with such technologies to streamline resource management processes and enhance overall project efficiency.
- Cultivate Communication Skills: Effective communication is critical in project resource management. HRs must be adept at conveying project requirements, expectations, and changes to team members. Clear communication fosters a collaborative environment and minimizes misunderstandings.
- Stay Informed About Industry Trends: To accurately forecast resource needs, HRs should stay informed about industry trends and emerging technologies. This knowledge enables them to anticipate the skills and resources that will be in demand for future projects.
- Encourage a Culture of Learning: HRs can foster a culture of continuous learning within the organization. This involves promoting training opportunities, encouraging certifications, and supporting professional development initiatives, ensuring that the project team remains adaptable and skilled.
Real-Life Examples:
- Google’s Project Oxygen: In one of the most innovative companies globally, Google’s HR team played a vital role in Project Oxygen. The initiative aimed to identify the key characteristics of effective managers within the organization. By leveraging HR expertise, Google identified the necessary leadership traits, enabling project leaders to select and develop managers who could effectively guide teams through complex projects. This strategic approach to talent management significantly contributed to Google’s project success.
- Tesla’s Gigafactory Construction: Tesla’s ambitious Gigafactory project required not only cutting-edge technology but also a highly skilled and motivated workforce. Tesla’s HR team, functioning as PRMs, meticulously identified the required skill sets for construction, operation, and maintenance roles. Through strategic talent acquisition, training programs, and performance management, HRs ensured that the Gigafactory project progressed seamlessly, highlighting the instrumental role HR plays in resource management for large-scale projects.
The Distinction: PRM vs. Project/Program Manager
While the roles of Project Resource Managers (PRMs), Project Managers (PMs), and Program Managers (PgMs) may sound similar, each carries distinct responsibilities in the project management ecosystem.
- Project Manager (PM): Project Managers focus on the overall planning, execution, and delivery of a specific project. They are responsible for defining project goals, creating schedules, and ensuring that the project is completed within scope, budget, and time constraints. PMs deal with the day-to-day aspects of project execution.
- Program Manager (PgM): Program Managers oversee multiple related projects, often with a broader organizational impact. They coordinate the interdependencies between projects within a program to ensure alignment with strategic goals. PgMs focus on achieving overarching business objectives through the successful execution of various projects.
- Project Resource Manager (PRM): Project Resource Managers, often operating within the HR domain, specialize in optimizing the allocation of resources for a project. They assess talent needs, facilitate team collaboration, and ensure that the right people with the right skills are available when needed. PRMs contribute to the success of projects by strategically managing human resources, aligning them with project goals.
Conclusion
Project resource management is a multifaceted task that requires a combination of skills, including talent acquisition, team building, and strategic planning. HR professionals, with their expertise in human capital management, are well-positioned to excel as Project Resource Managers. By developing project management skills, embracing technology, and fostering effective communication, HRs can contribute significantly to the success of projects and ensure optimal resource utilization. As organizations increasingly recognize the importance of strategic resource management, HR professionals play a pivotal role in shaping the future of project execution.