Social Cognitive Theory (SCT), developed by renowned psychologist Albert Bandura, is a comprehensive framework that seeks to explain how individuals acquire and apply knowledge, behavior, and attitudes through the interplay of social, cognitive, and environmental factors. This theory has become a cornerstone in the fields of psychology, education, and communication, offering valuable insights into the complex interactions that shape human behavior.
Key Concepts of Social Cognitive Theory:
- Observational Learning:
- One of the central tenets of SCT is observational learning, also known as modeling or imitation. Bandura posited that individuals learn by observing the actions and consequences of others. This process allows for the acquisition of new behaviors without direct experience.
- Reciprocal Determinism:
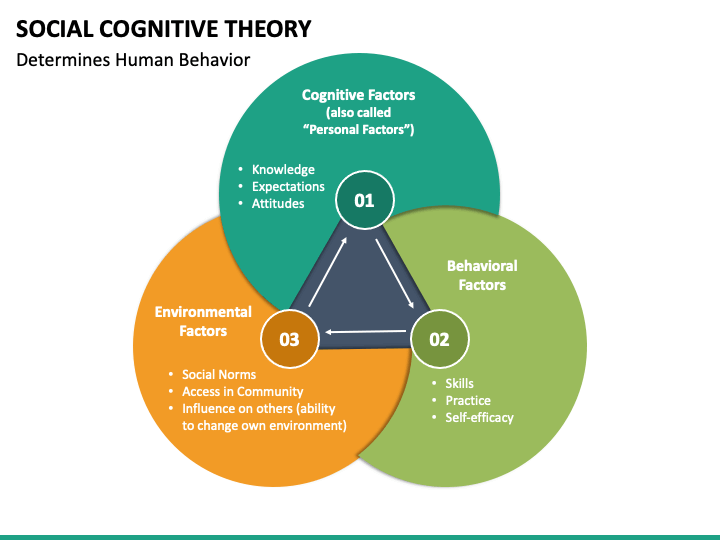
- SCT emphasizes the dynamic interplay between personal factors, behavior, and the environment. Reciprocal determinism suggests that these three components influence each other in a continuous feedback loop. For example, a person’s behavior can shape their environment, which, in turn, affects their cognition and subsequent actions.
- Self-efficacy:
- Self-efficacy is a crucial element in SCT, referring to an individual’s belief in their capability to perform a particular task or achieve a specific goal. Bandura highlighted the significance of self-efficacy in shaping motivation, effort, and persistence. High self-efficacy tends to lead to greater success and resilience in the face of challenges.
- Cognitive Processes:
- Cognitive processes play a pivotal role in SCT. Bandura emphasized attention, retention, reproduction, and motivation as key cognitive factors in observational learning. The learner must pay attention to the model, retain the information, be capable of reproducing the behavior, and possess the motivation to do so.
Applications of Social Cognitive Theory:
- Education:
- SCT has had a profound impact on educational practices. By understanding how observational learning and modeling influence student behavior, educators can design instructional strategies that promote positive learning outcomes. Additionally, fostering a sense of self-efficacy can enhance students’ confidence in their academic abilities.
- Health Behavior Change:
- In the realm of health psychology, SCT has been instrumental in designing interventions aimed at promoting healthier behaviors. By addressing self-efficacy, providing positive models, and creating supportive environments, health professionals can influence individuals to adopt and maintain healthier lifestyles.
- Media Influence:
- SCT is particularly relevant in the age of mass media. The theory helps explain how individuals can be influenced by the behaviors and attitudes portrayed in various media forms. Advertisers, for example, leverage SCT principles to model desired behaviors and shape consumer attitudes.
- Organizational Behavior:
- In the workplace, SCT can inform organizational practices related to training, leadership development, and employee motivation. By fostering a positive and supportive work environment, organizations can enhance employees’ self-efficacy and promote the acquisition of new skills through observational learning.
HR Use Cases:
Social Cognitive Theory also finds practical applications in the field of Human Resources (HR). In the context of talent development and management, SCT principles can guide HR professionals in designing effective training programs. By incorporating positive role models, providing clear expectations, and fostering a supportive learning environment, organizations can enhance employees’ observational learning experiences.
Moreover, SCT can be applied to leadership development within organizations. HR teams can utilize the theory to identify and promote effective leadership behaviors. By offering leadership training that emphasizes modeling desirable behaviors, organizations can help leaders build self-efficacy and enhance their ability to positively influence their teams.
Employee motivation is another area where SCT can be beneficial. Understanding the role of self-efficacy in shaping individuals’ motivation levels, HR professionals can implement strategies that boost employees’ belief in their capabilities. Recognition programs, mentorship opportunities, and clear career paths can contribute to higher self-efficacy and, consequently, increased motivation and job satisfaction.
Critiques and Future Directions:
While SCT has significantly contributed to our understanding of human behavior, it is not without its critiques. Some argue that the theory may oversimplify the complexity of human cognition and behavior, and others suggest that it does not sufficiently account for cultural and contextual influences.
Future research in the field may delve deeper into the cultural nuances that shape observational learning, explore the role of emotions in the learning process, and integrate advances in neuroscience to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the intricate mechanisms at play.
Conclusion:
Social Cognitive Theory has stood the test of time as a robust framework for understanding how individuals learn and develop. By emphasizing the interplay between social, cognitive, and environmental factors, SCT has practical applications in diverse fields, from education to health to organizational behavior. As researchers continue to explore and refine this theory, it remains a valuable tool for unraveling the intricate tapestry of human behavior and cognition, including its applications in optimizing HR practices for organizational success.