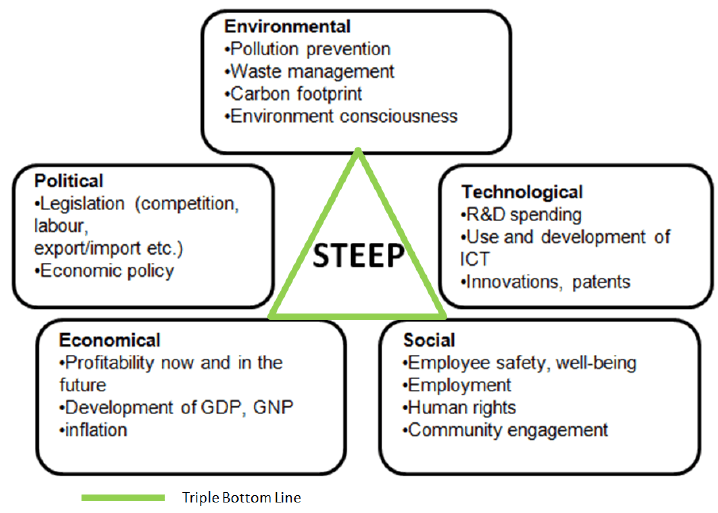
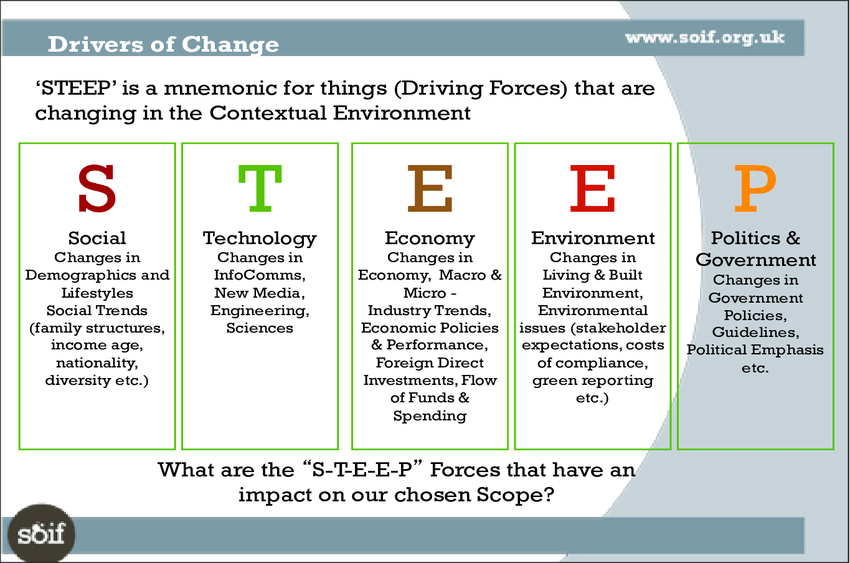
Step into the dynamic realm of Human Resources (HR), where navigating the ever-changing landscape is not just a challenge but a strategic imperative. Imagine a tool that acts as a compass, guiding HR professionals through the intricate maze of Social, Technological, Economic, Environmental, and Political factors. The STEEP model emerges as this indispensable guide, empowering HR leaders not only to decipher the external environment but also to craft strategies that resonate with the pulse of the evolving workplace. In this immersive journey, we unravel the layers of the STEEP model, backed by real-world examples that showcase its transformative impact on diverse HR scenarios. Get ready to explore HR horizons and witness the power of strategic excellence unfold.
- Social Factors: Adapting to Changing Workforce Dynamics
Social factors play a pivotal role in shaping the expectations and preferences of the modern workforce. Companies that successfully navigate these dynamics often emerge as employers of choice. Take the example of Google, a tech giant renowned for its progressive HR practices. Recognizing the importance of work-life balance, Google has implemented flexible work hours, remote work options, and onsite amenities, reflecting a deep understanding of social trends and employee needs.
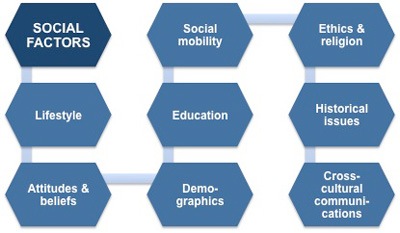
In a hypothetical scenario, a forward-thinking HR professional in a traditional manufacturing company observes the rising importance of work-life balance among employees. By advocating for flexible work arrangements and wellness programs, they not only enhance employee satisfaction but also position the company as a progressive and attractive employer.
- Technological Factors: Harnessing Innovation in HR Practices
Technological advancements have revolutionized the HR landscape, from recruitment processes to employee engagement initiatives. Amazon, a global e-commerce giant, exemplifies the integration of technology in HR. The company utilizes artificial intelligence in candidate screening, streamlining the hiring process and ensuring a data-driven approach to talent acquisition.
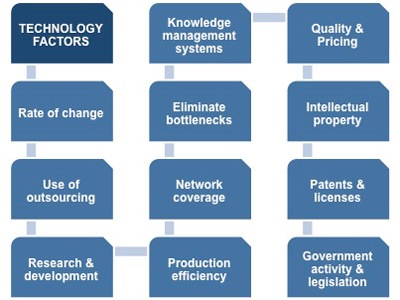
Consider a scenario where an HR leader in a mid-sized software development firm recognizes the potential of technology to enhance employee training. By implementing e-learning platforms, virtual reality simulations, or gamified training modules, the HR professional not only keeps the workforce abreast of technological advancements but also fosters a culture of continuous learning.
- Economic Factors: Strategic Talent Management in Dynamic Economies
Economic factors exert a profound influence on HR strategies, demanding agility and strategic thinking. During economic downturns, companies may face the challenge of cost-cutting and restructuring, requiring HR to manage talent effectively. IBM, a global technology and consulting company, is a prime example. During periods of economic uncertainty, IBM has strategically focused on reskilling and upskilling its workforce, ensuring it remains adaptable to changing economic landscapes.
In a hypothetical scenario, an HR leader in a retail company anticipates an economic downturn. Proactively, they implement cross-training programs to enhance the versatility of the workforce, preparing employees to take on different roles as the need arises. This strategic approach not only safeguards jobs but also positions the company for a quicker recovery when economic conditions improve.
- Environmental Factors: Fostering Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) in HR Practices
Environmental consciousness has permeated organizational values, prompting HR to incorporate sustainable practices. Patagonia, an outdoor clothing company, stands out for its commitment to environmental responsibility. The company’s HR policies reflect this commitment, offering employees paid time off for environmental activism and prioritizing sustainability in its supply chain.

In a scenario where an HR professional works for a manufacturing company, they recognize the growing importance of environmental sustainability. By introducing initiatives such as recycling programs, energy-efficient practices, or eco-friendly office designs, the HR leader not only aligns the company with environmental values but also engages employees in a shared commitment to corporate social responsibility.
- Political Factors: Navigating Regulatory Landscapes and Global Dynamics
Political factors, including government policies and geopolitical events, significantly impact the legal and regulatory framework within which HR operates. Multinational corporations often face the challenge of navigating diverse political environments. Microsoft, a global technology company, exemplifies adept handling of political factors. Microsoft’s HR practices are designed to comply with diverse global regulations, ensuring consistency and fairness across its international workforce.
In a hypothetical scenario, an HR professional in an international financial institution navigates changes in immigration policies. By collaborating with legal experts, the HR leader ensures the seamless relocation of international talent and provides necessary support to employees facing immigration challenges, showcasing the importance of HR agility in the face of political shifts.
Conclusion:
The STEEP model serves as a compass, guiding HR professionals through the intricate external factors that shape the workplace. As evidenced by real-world examples, companies that proactively incorporate social, technological, economic, environmental, and political considerations into their HR strategies emerge as industry leaders. In the hypothetical scenarios presented, HR professionals play a pivotal role in adapting to societal shifts, harnessing technological innovation, strategically managing talent in economic uncertainties, fostering environmental responsibility, and navigating complex political landscapes.
In an era of constant change, HR’s ability to leverage the insights provided by the STEEP model not only ensures organizational resilience but also positions companies as employers of choice in the competitive talent market. As HR continues to evolve, the STEEP model remains an invaluable tool for practitioners to craft strategies that not only respond to current challenges but also anticipate and embrace future trends in the ever-evolving world of work.