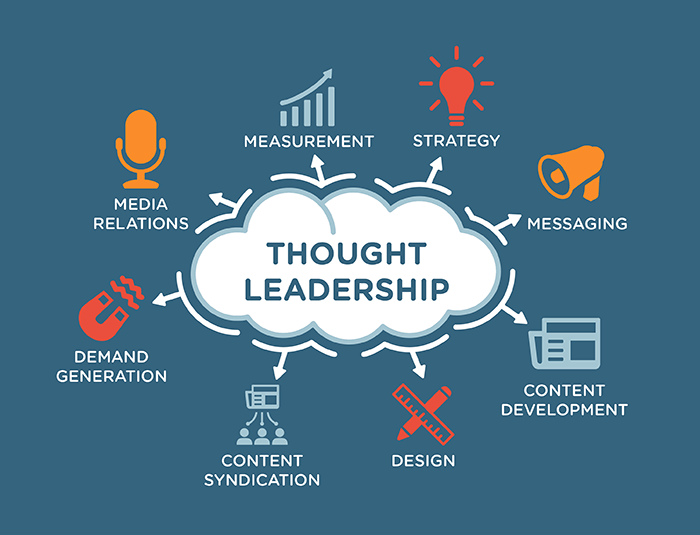
The significance of equipping every employee with effective learning has taken center stage in the ever-changing face of the modern workplace. Thought leaders from various industries are having a deep discussion about how to create an atmosphere in which learning is more than just a buzzword but a transformative force that propels both individuals and businesses to excellence.

A) Unveiling the Power of Thought Leadership:
Thought leadership is not merely about possessing knowledge; it’s about actively shaping the future by sharing insights that inspire and drive positive change. In the realm of empowering employees through meaningful learning experiences, thought leaders are focusing on strategies that go beyond traditional training paradigms.
Defining Thought Leadership:
Thought leadership is more than a mere buzzword; it encapsulates the essence of being at the forefront of industry discourse, offering valuable insights, and driving meaningful change. Thought leaders are individuals or entities recognized for their expertise, innovation, and the ability to influence others through their perspectives and ideas.
Key Elements of Thought Leadership:
- Expertise and Authority:
- Thought leaders are experts in their respective fields. Whether in technology, finance, healthcare, or any other domain, they possess a deep understanding of industry trends, challenges, and opportunities. Their expertise establishes them as trusted authorities, and their insights carry weight within their communities.
- Innovation and Vision:
- Thought leaders are not confined to the status quo; they are visionaries who foresee the future and propose innovative solutions. Their ability to think beyond current paradigms and anticipate trends positions them as catalysts for change.
- Effective Communication:
- Thought leadership is not just about having ideas; it’s about communicating them effectively. Thought leaders possess strong communication skills, conveying complex concepts in a compelling and accessible manner. Whether through articles, speeches, or social media, they engage their audience with clarity and impact.
- Consistency and Authenticity:
- Consistency is a hallmark of thought leadership. Thought leaders don’t emerge overnight; they build their influence through a sustained commitment to sharing valuable insights. Authenticity is equally crucial – thought leaders are genuine, transparent, and aligned with their core values.
- Impact on Industry Discourse:
- Thought leaders contribute to and shape industry conversations. They offer fresh perspectives, challenge existing norms, and provide thought-provoking insights that elevate the discourse within their fields.
Unveiling the Power of Thought Leadership:
- Driving Innovation:
- Thought leaders are instrumental in driving innovation. Their ability to envision new possibilities and challenge conventional thinking sparks creativity within their industries. As catalysts for change, thought leaders inspire others to push boundaries and explore uncharted territories.
- Building Credibility and Trust:
- Thought leadership builds credibility and trust. When individuals or organizations consistently offer valuable insights and solutions, they earn the trust of their audience. This trust, once established, becomes a foundation for long-term relationships and collaborations.
- Attracting Talent and Opportunities:
- Thought leaders naturally attract top talent and opportunities. Their influence extends beyond their immediate circles, drawing in individuals who are eager to be part of innovative and forward-thinking initiatives. Thought leaders become magnets for talent and collaborations that drive growth.
- Shaping Industry Trends:
- Thought leaders are trendsetters. Their ability to identify emerging trends and articulate their implications positions them as influential figures who shape the direction of their industries. Through thought leadership, they become architects of the future.
- Educating and Empowering:
- Thought leaders play a crucial role in educating their audience. By sharing knowledge, insights, and best practices, they empower others to navigate challenges and seize opportunities. Thought leadership is, at its core, a commitment to the education and development of the broader community.
B) The Changing Face of Workplace Learning:
In the past, workplace learning often followed a one-size-fits-all model, leaving some employees disengaged and others underserved. However, the dynamics are shifting, and the emphasis is now on customization and personalization. Thought leaders are championing a learner-centric approach, recognizing that each employee brings a unique set of skills, aspirations, and learning preferences to the table.
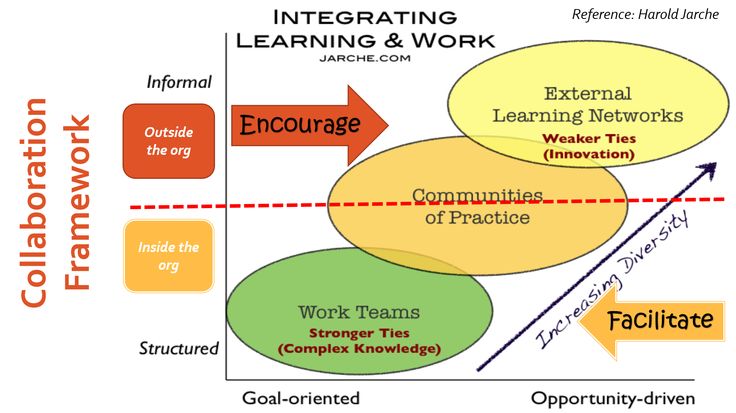
In the digital era, the workplace is undergoing a transformative shift, and so too is the landscape of workplace learning. As we stand on the cusp of unprecedented change, the insights and philosophies of thought leaders like Harold Jarche illuminate the path forward. Let’s embark on a journey to explore the changing face of workplace learning, where adaptability, collaboration, and continuous improvement take center stage.
Harold Jarche’s Influence:
Harold Jarche, a renowned thought leader in the realm of workplace learning, brings a unique perspective to the table. His model of Personal Knowledge Mastery (PKM) emphasizes the importance of individual agency and continuous sense-making in the learning process. Jarche’s work underscores the need for a shift from traditional, top-down learning models to more agile, networked approaches.
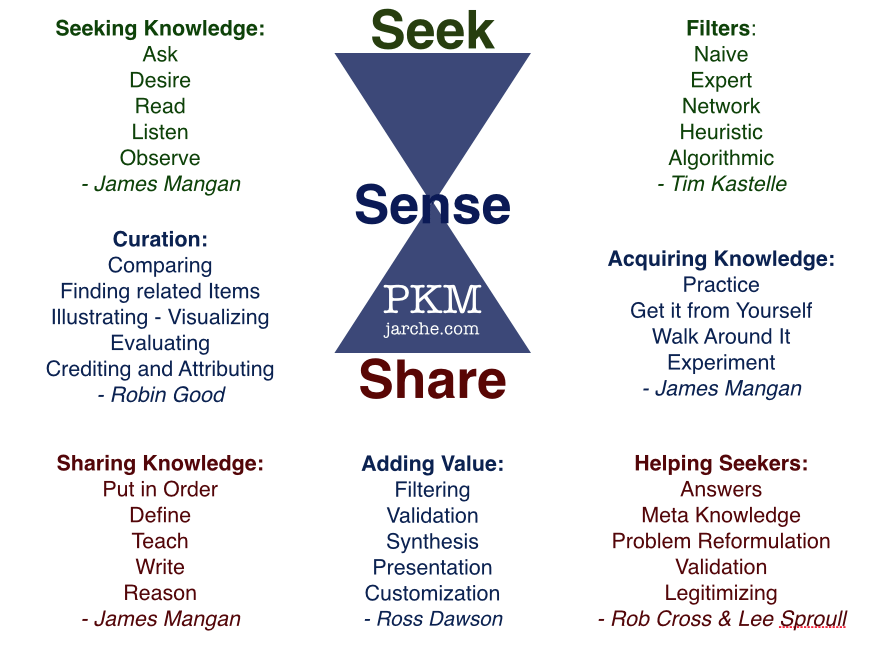
From Formal to Informal Learning:
The traditional paradigm of workplace learning often revolved around formal, structured programs. However, the changing face of the workplace is marked by a shift towards informal learning. This involves a more organic, bottom-up approach where employees actively seek, create, and share knowledge within their networks.
Jarche’s concept of the “Learning Network” aligns with this trend, highlighting the significance of building connections and collaborating with peers to foster a culture of continuous learning. Learning is no longer confined to scheduled training sessions but occurs in the flow of work, driven by the daily challenges and opportunities encountered on the job.
Adaptive Learning Ecosystems:
In the changing face of workplace learning, the emergence of adaptive learning ecosystems is notable. Organizations are moving away from one-size-fits-all approaches to embrace personalized, adaptive learning platforms. These platforms leverage technology to tailor learning experiences based on individual needs, preferences, and performance.
Jarche’s PKM model complements this shift by putting the onus on individuals to curate their own knowledge. It empowers employees to navigate the vast sea of information, filter what is relevant, and create a personalized knowledge framework that evolves over time. This adaptability is crucial in an era where skills become obsolete at an unprecedented pace.
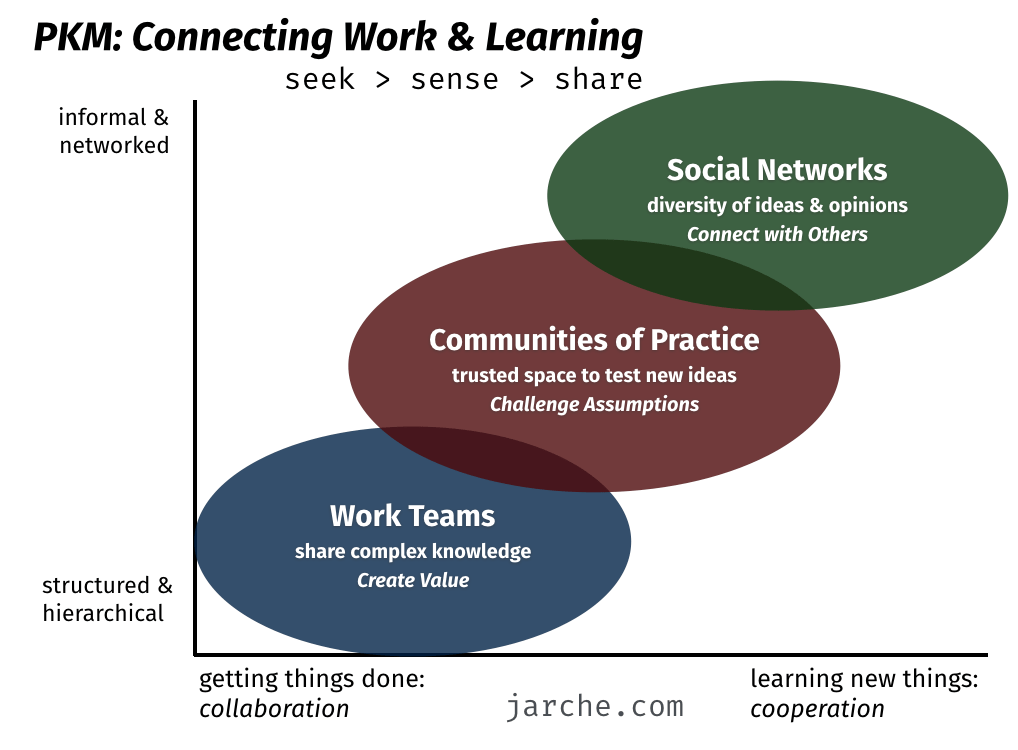
Continuous Learning and the 70-20-10 Model:
Jarche’s perspective resonates with the 70-20-10 model, which suggests that 70% of learning happens through on-the-job experiences, 20% through social interactions, and 10% through formal education. This model challenges the traditional overemphasis on formal training and encourages organizations to create environments that facilitate experiential learning and social collaboration.
Organizations are increasingly recognizing the need to provide platforms for employees to share tacit knowledge, engage in mentorship, and participate in communities of practice. The changing face of workplace learning involves creating spaces where the wisdom of experienced employees is harnessed and shared organically, contributing to the collective intelligence of the organization.
Technology as an Enabler:
The changing face of workplace learning is inseparable from technological advancements. From virtual reality simulations to artificial intelligence-driven adaptive learning systems, technology is playing a pivotal role in shaping the future of learning. Jarche’s emphasis on the integration of technology aligns with the industry’s movement towards digital platforms that facilitate collaboration, knowledge sharing, and real-time learning.
C) Nurturing a Culture of Continuous Learning:
One key aspect of empowering employees is fostering a culture of continuous learning. Thought leaders stress the significance of creating an environment where learning is not confined to occasional training sessions but becomes an integral part of the organizational DNA. This culture encourages curiosity, innovation, and adaptability, essential elements for thriving in today’s fast-paced business landscape.
Defining Continuous Learning:
Continuous learning is more than just a series of training sessions or occasional workshops; it’s a philosophy that embraces the idea that learning is a lifelong journey. In a workplace context, it involves the ongoing development of skills, knowledge, and competencies, fostering an environment where individuals are encouraged to acquire new insights, refine existing skills, and adapt to emerging challenges.
Key Components of a Culture of Continuous Learning:
- Leadership Commitment:
- The commitment to continuous learning starts at the top. Leaders play a pivotal role in setting the tone for the organization. When leaders prioritize and actively participate in ongoing learning initiatives, it sends a powerful message to the entire workforce.
- Accessible Learning Resources:
- Organizations need to provide easy access to diverse learning resources. This includes online courses, workshops, webinars, and other materials that cater to different learning styles. The resources should be readily available and aligned with the organization’s goals and industry trends.
- Promoting a Growth Mindset:
- A culture of continuous learning is grounded in a growth mindset. Encouraging employees to embrace challenges, persist in the face of setbacks, and see effort as the path to mastery creates an environment where learning is celebrated, and mistakes are viewed as opportunities for improvement.
- Encouraging Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing:
- Learning is not a solitary activity. Fostering collaboration and creating platforms for knowledge sharing are integral to a culture of continuous learning. When employees share their expertise, experiences, and insights, it enriches the collective knowledge of the organization.
- Feedback and Reflection:
- Regular feedback and opportunities for reflection are crucial elements. Constructive feedback helps individuals understand their strengths and areas for improvement, while reflection allows employees to consolidate their learning and apply it in a meaningful way.
- Adaptability and Flexibility:
- A culture of continuous learning is inherently adaptable. It embraces change and is flexible in response to evolving industry trends and organizational needs. This adaptability is essential for staying relevant and competitive in today’s dynamic business environment.
- Recognition and Rewards for Learning:
- Acknowledging and rewarding learning achievements creates a positive feedback loop. This can take the form of formal recognition programs, badges, or other incentives that highlight the value placed on continuous learning within the organization.
Implementing Continuous Learning in Practice:
- Developing Learning Plans:
- Individualized learning plans that align with both organizational and personal goals are instrumental. Employees, in collaboration with their managers, can identify areas for development and chart a course for continuous learning.
- Mentorship Programs:
- Mentorship fosters a culture of learning from one another. Establishing mentorship programs connects experienced employees with those seeking guidance, creating a knowledge-sharing ecosystem that benefits both mentors and mentees.
- Learning Management Systems (LMS):
- Implementing Learning Management Systems streamlines the delivery and tracking of learning initiatives. These systems provide a centralized hub for courses, assessments, and progress tracking, ensuring a cohesive and organized approach to continuous learning.
- Incorporating Learning into Performance Reviews:
- Linking continuous learning with performance evaluations reinforces its importance. By assessing an individual’s commitment to learning and development during performance reviews, organizations send a clear message about the value placed on ongoing skill enhancement.
Measuring the Impact of Continuous Learning:
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
- Defining KPIs related to continuous learning helps organizations measure its impact. This could include metrics such as the completion rates of training programs, improvements in specific skills, or the application of learning in daily tasks.
- Employee Engagement Surveys:
- Employee engagement surveys can provide insights into the perceived value of continuous learning initiatives. Feedback on the relevance, accessibility, and effectiveness of learning programs can guide improvements and refinements.
- Business Impact:
- Ultimately, the success of continuous learning should translate into tangible business outcomes. Whether it’s improved employee performance, enhanced innovation, or increased adaptability to market changes, organizations should assess how continuous learning contributes to their overall success.
D) Thought Leaders on the Forefront:
Prominent thought leaders, including industry experts and forward-thinking CEOs, are actively contributing to the discourse on empowering employees with learning that works. Their insights revolve around several key principles:
- Personalization and Adaptability:
Thought leaders emphasize the need to tailor learning experiences to individual preferences.
Adaptive learning technologies are gaining prominence, ensuring that each employee can learn at their own pace and style. - Alignment with Organizational Goals:
Learning initiatives should be closely aligned with the strategic goals of the organization.
Thought leaders argue that effective learning is not just about acquiring knowledge but about applying it to drive business success. - Technology as an Enabler:
The role of technology in learning is a recurring theme among thought leaders.
Platforms leveraging artificial intelligence and virtual reality are being hailed as tools that can revolutionize the learning experience. - Leadership Development:
Thought leaders stress the importance of developing leadership skills at all levels of the organization.
Leadership training programs are seen as investments in the long-term success and sustainability of a business. - Measuring Impact:
Metrics and analytics play a crucial role in evaluating the effectiveness of learning initiatives.
Thought leaders advocate for a shift from traditional performance metrics to more holistic measures that encompass skills development and employee engagement.
Case Study: Motilal Oswal Financial Services
In the financial services sector, Motilal Oswal Financial Services stands out as an exemplar in empowering its employees through innovative learning initiatives. By aligning learning programs with its mission and values, the company ensures that every employee is equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary to navigate the complexities of the financial industry.
Motilal Oswal’s commitment to continuous learning is evident in its investment in cutting-edge technologies for employee development. The company has embraced adaptive learning platforms, providing personalized training modules that cater to the diverse needs of its workforce. This not only enhances employee engagement but also contributes to the overall growth and success of the organization.
Motilal Oswal Financial Services has emerged as a trailblazer in the financial sector, epitomizing the fusion of innovative learning methodologies with a commitment to its mission and values. At the core of Motilal Oswal’s approach is the recognition that the financial industry demands not only technical acumen but also a profound understanding of market dynamics and client needs.
1. Personalized Learning Paths:
Motilal Oswal’s learning initiatives prioritize personalization. The company has implemented adaptive learning platforms that tailor modules based on individual learning styles, ensuring that each employee receives a bespoke educational experience. This commitment to personalization extends beyond technical skills, encompassing soft skills crucial for effective client interactions.
2. Technological Integration:
Motilal Oswal has embraced cutting-edge technologies, leveraging artificial intelligence and virtual reality to enhance the learning journey. Virtual trading simulations, for instance, allow employees to practice in real-world market scenarios, honing their decision-making skills. This integration of technology not only enriches learning experiences but also aligns with the company’s forward-thinking ethos.
3. Leadership Development as a Cornerstone:
Motilal Oswal recognizes that sustainable success hinges on leadership at all levels. The company invests significantly in leadership development programs, ensuring that employees are not merely well-versed in their roles but also equipped with the skills to guide teams and navigate industry challenges.
4. Mission and Values Alignment:
Motilal Oswal’s learning initiatives are intricately woven into the fabric of its mission and values. By aligning educational programs with the company’s overarching goals, employees are not only acquiring knowledge but also imbibing the ethos that drives Motilal Oswal’s success.
5. Measuring Impact Beyond Traditional Metrics:
Motilal Oswal adopts a holistic approach to measure the impact of learning initiatives. While traditional metrics are essential, the company recognizes the significance of evaluating the real-world application of acquired skills and the correlation with enhanced client satisfaction and business outcomes.
Case Study: Google
Google’s learning culture is renowned for its innovative and forward-thinking approach to employee development. Rooted in the company’s core values of creativity, curiosity, and a commitment to continuous improvement, Google’s approach to learning goes beyond traditional training programs. It is characterized by flexibility, inclusivity, and a recognition of the importance of nurturing individual growth to drive overall organizational success.
Foundations of Google’s Learning Culture:
- Google University:
- At the heart of Google’s learning culture is “Google University,” an internal platform that provides employees with access to a vast array of courses. These courses cover a spectrum of subjects, ranging from technical skills to personal development and leadership.
- Innovation and Adaptability:
- Google’s learning initiatives are deeply rooted in its culture of innovation. The company places a premium on staying ahead of the curve in the ever-evolving tech landscape. Employees are encouraged to explore emerging technologies and acquire new skills to remain at the forefront of industry trends.
- 20% Time:
- One of the most iconic aspects of Google’s learning culture is the “20% time” policy. Engineers and other employees are encouraged to spend 20% of their working hours on projects that personally interest them or contribute to the company’s goals. This dedicated time fosters a culture of self-directed learning and creativity.
Key Features of Google’s Learning Culture:
- Holistic Approach:
- Google’s learning initiatives are not solely focused on technical skills. While technical proficiency is crucial, the company recognizes the importance of holistic development. Courses cover a wide range of topics, including communication skills, leadership development, and personal well-being.
- GoogleEDU:
- GoogleEDU is an umbrella initiative encompassing various learning programs within the organization. It includes technical training, leadership development courses, and workshops on soft skills. This centralized approach ensures that learning opportunities are easily accessible to all employees.
- Learning Platforms:
- Google utilizes a variety of learning platforms to cater to different learning styles. Whether through traditional classroom training, online courses, or interactive workshops, employees have the flexibility to choose the format that best suits their preferences.
- Learning from Failure:
- Google’s culture encourages risk-taking and learning from failure. Employees are not penalized for well-intentioned failures; instead, these experiences are viewed as opportunities for growth and improvement.
- Leadership Development:
- Google places a significant emphasis on leadership development at all levels. The company recognizes that effective leadership is pivotal for sustained success. Leadership programs include mentorship, coaching, and immersive experiences to hone leadership skills.
Continuous Learning in Action:
- Career Mobility:
- Google promotes career mobility, allowing employees to explore different roles within the organization. This not only provides diverse learning experiences but also fosters a culture of adaptability and versatility.
- Tech Talks and Workshops:
- Google frequently organizes tech talks and workshops featuring industry experts. These events serve as forums for employees to engage with cutting-edge technologies, trends, and advancements in their respective fields.
- Learning Resource Accessibility:
- Google ensures that learning resources are easily accessible to all employees. Whether through internal databases, learning portals, or partnerships with external educational institutions, the company strives to democratize access to knowledge.
Impact on Employee Engagement and Innovation:
Google’s commitment to a robust learning culture has a profound impact on employee engagement and innovation:
- Increased Employee Satisfaction:
- Employees at Google often express high levels of job satisfaction, attributing it to the opportunities for personal and professional growth facilitated by the company’s learning initiatives.
- Innovation and Creativity:
- The 20% time policy, coupled with a culture that values experimentation, has been instrumental in fostering a spirit of innovation. Many of Google’s groundbreaking products, such as Gmail and Google Maps, originated from these passion projects.
- Adaptability to Industry Changes:
- Google’s learning culture equips employees with the skills and mindset needed to adapt to rapid changes in the tech industry. This adaptability is a key factor in Google’s ability to maintain its position as a global tech leader.
Challenges and Future Directions:
While Google’s learning culture is widely praised, it is not without its challenges. The company continuously evolves its approach to address emerging needs and trends. Future directions may include a deeper integration of artificial intelligence in learning platforms, enhanced focus on diversity and inclusion in learning initiatives, and further exploration of experiential learning opportunities.
In conclusion, Google’s learning culture stands as a testament to the belief that fostering a culture of continuous learning is not just a means of skill acquisition but a strategic imperative for organizational success. By championing innovation, adaptability, and holistic development, Google provides a blueprint for organizations seeking to cultivate a dynamic and thriving learning culture in the ever-changing landscape of the modern workplace.
Case Study: Toyota’s Kaizen Philosophy
Toyota’s Kaizen philosophy, deeply rooted in Japanese culture, has become synonymous with continuous improvement and efficiency in the business world. The term “Kaizen” translates to “change for the better” or “continuous improvement” and is at the core of Toyota’s organizational culture. This philosophy extends beyond manufacturing processes to influence every aspect of the company’s operations, promoting a mindset of relentless improvement, waste reduction, and employee involvement.
Foundations of Kaizen:
- Historical Roots:
- Kaizen has its roots in post-World War II Japan when Toyota faced economic challenges. The company’s leaders, including Taiichi Ohno and Shigeo Shingo, developed the Kaizen philosophy as a response to the need for economic efficiency and quality improvement.
- Continuous Improvement:
- At its essence, Kaizen emphasizes incremental and continuous improvement. It encourages employees at all levels to consistently seek ways to enhance processes, eliminate waste, and optimize efficiency.
Key Principles of Toyota’s Kaizen Philosophy:
- Respect for People:
- Kaizen places a profound emphasis on respecting every individual within the organization. It encourages open communication, collaboration, and valuing the input of every employee.
- Elimination of Waste (Muda):
- A fundamental tenet of Kaizen is the identification and elimination of waste in all forms. This includes wasted time, resources, and materials. By reducing waste, Toyota not only improves efficiency but also minimizes costs.
- Standardization and Consistency:
- Kaizen emphasizes the importance of standardized work processes. Standardization ensures consistency and provides a baseline for continuous improvement efforts. It also facilitates easier identification of deviations that may need improvement.
- Continuous Problem Solving:
- Kaizen encourages a proactive approach to problem-solving. Rather than waiting for major issues to arise, employees are empowered to identify and address problems on an ongoing basis. This prevents the accumulation of challenges and fosters a culture of continuous problem resolution.
- Just-In-Time (JIT) Production:
- JIT is a key aspect of Kaizen, focusing on producing only what is needed, when it is needed, and in the necessary quantity. This minimizes inventory, reduces lead times, and enhances overall production efficiency.
- Employee Involvement:
- Every employee is considered a valuable contributor to the improvement process. Kaizen promotes a sense of ownership and responsibility among employees, encouraging them to actively participate in identifying and implementing improvements.
Kaizen in Action:
- Kaizen Events (Kaizen Blitz):
- Toyota often organizes Kaizen events, also known as Kaizen Blitz, where cross-functional teams come together to intensely focus on solving a specific problem or improving a particular process within a short time frame. These events foster collaboration and rapid problem-solving.
- Gemba Walks:
- The concept of “Gemba” refers to the actual place where work is done. Toyota leaders regularly conduct Gemba walks, going to the shop floor to observe processes, ask questions, and gain insights directly from the employees engaged in the work. This hands-on approach enhances communication and promotes a deeper understanding of the challenges and opportunities for improvement.
- Kaizen Teian (Suggestion) System:
- Toyota encourages employees to submit improvement suggestions through the Kaizen Teian system. This system allows employees to share their ideas for process improvement, and those ideas are systematically evaluated and implemented if found beneficial.
Impact and Success of Kaizen:
- Quality Improvement:
- Kaizen has played a pivotal role in Toyota’s reputation for producing high-quality vehicles. The philosophy’s focus on continuous improvement and problem-solving has resulted in enhanced product quality and reliability.
- Efficiency and Cost Reduction:
- By systematically eliminating waste and optimizing processes, Toyota has achieved significant gains in efficiency. This, in turn, has contributed to cost reduction and improved competitiveness.
- Employee Engagement:
- Kaizen’s emphasis on employee involvement and empowerment fosters a culture of engagement and commitment. Employees feel a sense of ownership in the improvement process, leading to increased job satisfaction and motivation.
- Adaptability to Change:
- Kaizen equips Toyota with the flexibility to adapt to changing market conditions and customer preferences. The continuous improvement mindset allows the company to stay ahead of the curve and respond rapidly to evolving business landscapes.
Challenges and Future Applications:
While Kaizen has been instrumental in Toyota’s success, it is not without challenges. Implementing a continuous improvement philosophy requires a cultural shift and ongoing commitment. Looking to the future, Toyota continues to explore ways to integrate digital technologies, such as Industry 4.0 practices, to enhance and streamline Kaizen processes.
Conclusion:
Toyota’s Kaizen philosophy represents a timeless commitment to the pursuit of excellence through continuous improvement. Beyond being a set of tools and methodologies, Kaizen is a mindset that permeates every level of the organization. Its enduring impact on Toyota’s success serves as a testament to the transformative power of a culture dedicated to relentless improvement, waste reduction, and the empowerment of every individual within the organization. As businesses globally seek strategies for sustainable growth, the principles of Kaizen offer valuable insights into fostering a culture of continuous improvement and adaptability in the face of an ever-changing business landscape.
Case Study: Salesforce’s Trailhead Platform
Salesforce’s Trailhead is a groundbreaking online learning platform that revolutionizes the way individuals acquire and enhance their skills in the realm of customer relationship management (CRM) and other Salesforce-related technologies. Launched by Salesforce, a global leader in cloud-based software solutions, Trailhead provides a dynamic, gamified, and interactive approach to learning, empowering users to master Salesforce technologies at their own pace. This detailed exploration delves into the key features, impact, and success of the Trailhead platform.
Key Features of Salesforce’s Trailhead:
- Gamification and Points System:
- Trailhead employs gamification to make learning engaging and fun. Users earn points, badges, and even virtual “trailblazer ranks” as they complete modules, projects, and assessments. This gamified approach motivates learners and fosters a sense of accomplishment.
- Interactive Learning Paths (Trails):
- Learning on Trailhead is organized into learning paths known as “trails.” These trails guide users through a series of modules, projects, and challenges designed to build specific skills or knowledge areas. Trails cover a wide range of topics, from introductory concepts to advanced technical skills.
- Hands-On Challenges and Projects:
- One of Trailhead’s distinctive features is its emphasis on hands-on learning. Users can apply what they’ve learned in a sandbox environment, solving real-world business scenarios through hands-on challenges and projects. This practical approach ensures that learners gain practical, job-ready skills.
- Modules for All Skill Levels:
- Trailhead caters to users of all skill levels, from beginners to seasoned professionals. Modules are labeled with different difficulty levels, allowing learners to progress at their own pace. This inclusivity makes Trailhead an accessible resource for anyone interested in Salesforce technologies.
- Role-Based Learning Paths:
- Trailhead offers role-based learning paths tailored to different job roles within the Salesforce ecosystem. Whether one is a developer, administrator, business analyst, or marketer, there are specialized trails designed to meet the specific needs of each role.
- Community and Collaboration:
- Trailhead fosters a sense of community among learners. Users can connect with each other through discussion forums, share their achievements, and seek advice. This collaborative aspect enhances the learning experience by providing opportunities for networking and knowledge exchange.
- Trailhead Playground:
- The Trailhead Playground is a dedicated environment where users can experiment with Salesforce technologies in a risk-free space. This enables hands-on exploration and experimentation, allowing users to apply concepts in a practical setting without affecting their live Salesforce instance.
- Certification Preparation:
- Trailhead serves as an excellent resource for those preparing for Salesforce certifications. Specialized trails and modules are crafted to align with certification exams, providing a structured and comprehensive approach to exam preparation.
Impact and Success of Trailhead:
- Skills Development and Career Advancement:
- Trailhead has played a pivotal role in equipping individuals with the skills needed to thrive in the Salesforce ecosystem. Users can enhance their proficiency, stay updated on the latest features and technologies, and advance their careers within the Salesforce community.
- Increased Adoption of Salesforce Technologies:
- Trailhead has contributed to the increased adoption of Salesforce technologies by making it accessible and approachable. Organizations leverage Trailhead to train their teams, ensuring that employees are proficient in using Salesforce tools and contributing to the success of CRM implementations.
- Trailblazer Community:
- The sense of community fostered by Trailhead is a testament to its success. The Trailblazer Community, as it’s known, brings together professionals, developers, administrators, and enthusiasts who share a common interest in Salesforce technologies. This vibrant community serves as a valuable support network for individuals at all stages of their careers.
- Recognized Industry-Wide:
- Trailhead has received widespread recognition and accolades within the industry. Its innovative approach to learning has garnered praise, and it has become a benchmark for other organizations looking to develop engaging and effective online learning platforms.
Trailhead’s Role in Skill Development and Inclusion:
- Accessibility and Inclusivity:
- Trailhead is designed to be inclusive, providing equal opportunities for learning regardless of one’s background or location. The platform’s accessibility features, multilingual content, and varied learning formats contribute to its inclusivity.
- Addressing the Skills Gap:
- Trailhead addresses the skills gap in the technology sector by offering a platform where individuals can acquire in-demand skills. This is particularly crucial in the rapidly evolving field of Salesforce technologies, where staying current is essential.
Challenges and Future Developments:
While Trailhead has been successful, it is not without challenges. Some users may face difficulties with certain advanced topics or seek more in-depth content. Salesforce continues to address these challenges by regularly updating and expanding Trailhead content to meet the evolving needs of its user base.
Conclusion:
Salesforce’s Trailhead has redefined online learning by combining innovation, gamification, and practicality to create an engaging and effective platform. Its impact on skills development, career advancement, and the Salesforce community at large is evident. As organizations and individuals navigate the evolving landscape of technology, Trailhead stands as a shining example of how online learning can be a catalyst for empowerment, inclusion, and continuous growth within the dynamic world of Salesforce technologies. Whether you are a beginner exploring CRM concepts or an experienced professional aiming for certification, Trailhead provides a trailblazing journey towards mastering Salesforce technologies.
The Road Ahead:
As the conversation on empowering every employee with effective learning gains momentum, thought leaders are looking toward the future with a sense of optimism and purpose. The journey involves breaking away from traditional molds, embracing technology, and fostering a culture where learning is a shared responsibility.
In conclusion, the thought leadership conversation on empowering every employee with learning that works is a journey toward excellence and sustainability. By prioritizing personalization, aligning with organizational goals, leveraging technology, investing in leadership development, and measuring impact, businesses can create an environment where every employee is not just a contributor but a driving force in the pursuit of success. Through collaborative efforts and a commitment to continuous improvement, organizations can truly cultivate a culture of learning that propels them to new heights in an ever-changing world.