The ever-evolving landscape of project management is witness to the prominence of various methodologies designed to align organizational processes with strategic goals. In this extensive exploration, we delve into the nuances of project management frameworks, focusing on Lean, Just-in-Time (JIT), Six Sigma, Design Thinking, Agile, and additional methodologies like Design for Six Sigma (DFSS). The objective is to provide a nuanced understanding of when and how these frameworks can be optimally employed within Human Resources (HR) functions.
Lean Project Management: Streamlining Efficiency in HR
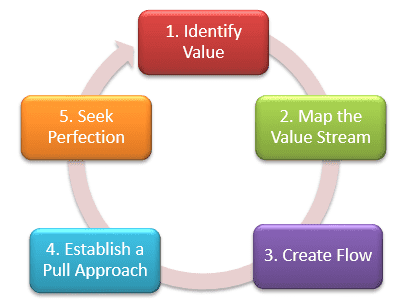
Lean project management, inspired by lean manufacturing principles, seeks to eliminate waste and optimize efficiency. The pillars of Lean include identifying value, mapping the value stream, creating flow, establishing pull, and pursuing perfection. In HR, Lean principles can revolutionize processes, such as recruitment, onboarding, and training.
Scenario: Enhancing Recruitment Processes
Application: Lean principles are employed by an HR team to improve the recruitment process. By identifying and eliminating non-value-adding activities, like redundant paperwork and unnecessary interviews, the team effectively reduces time-to-hire and enhances overall recruitment efficiency.
Just-in-Time (JIT) Project Management: Precision Timing in HR
JIT project management centers around delivering products or services exactly when needed, minimizing inventory and storage costs. In HR, JIT principles can be harnessed to optimize training programs, ensuring that employees receive necessary training precisely when required.
Scenario: On-the-Job Training
Application: An HR department embraces JIT principles for training new employees. Instead of conducting extensive training sessions beforehand, the team provides on-the-job training as needed, reducing downtime and ensuring employees acquire skills precisely when relevant.
Six Sigma Project Management: Striving for Perfection in HR Processes
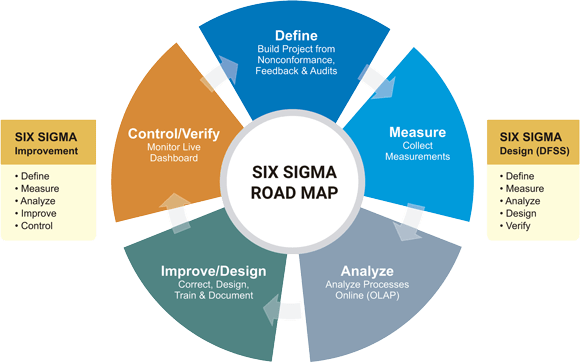
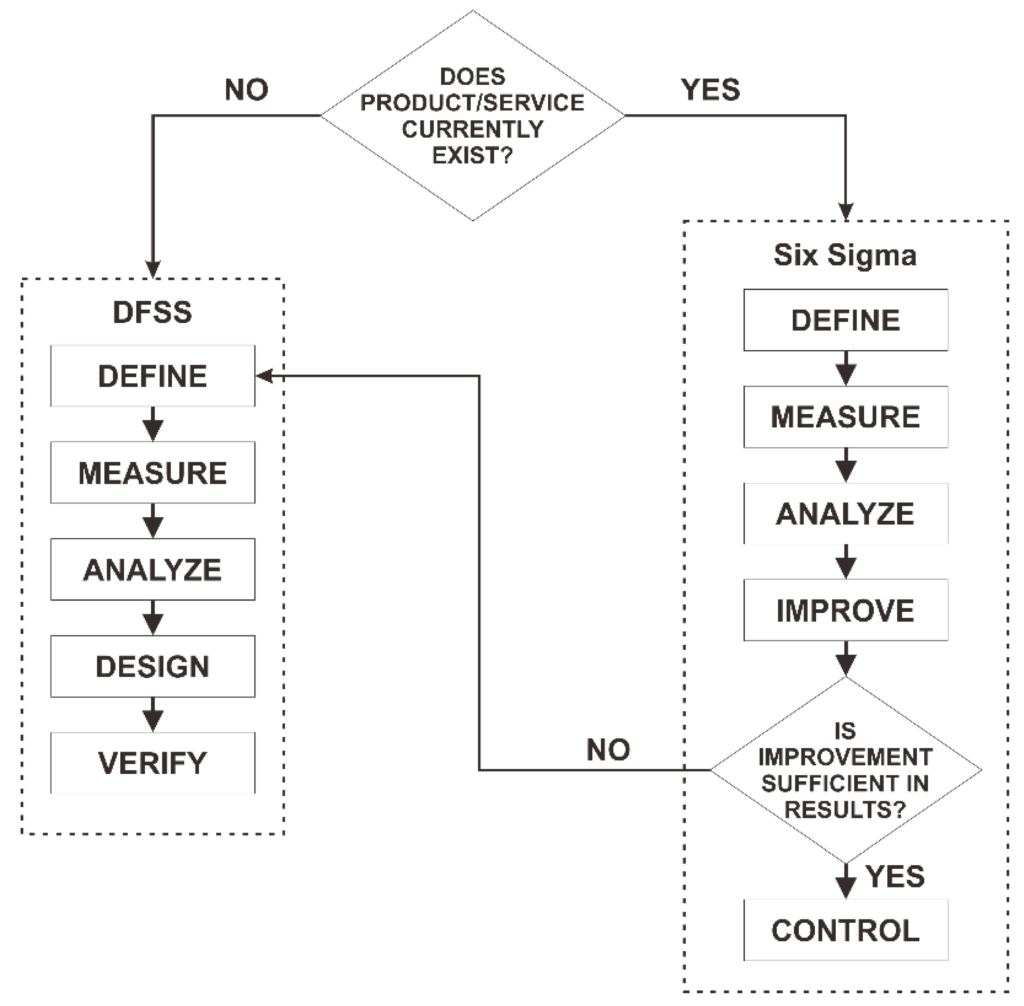
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology aimed at improving process efficiency and reducing defects. It employs two primary frameworks – DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) and DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, Verify). In HR, Six Sigma can be instrumental in enhancing the accuracy and effectiveness of processes like performance evaluations and talent acquisition.
Scenario: Performance Appraisal Enhancement
Application: The HR team utilizes the DMAIC framework to improve the performance appraisal process. By defining key metrics, measuring current performance, analyzing areas of improvement, implementing changes, and establishing control measures, the team enhances the accuracy and fairness of performance evaluations.
Design Thinking in Project Management: A Human-Centered Approach in HR
Design Thinking is a human-centered approach emphasizing empathy, ideation, and prototyping to solve complex problems. In HR, Design Thinking can be applied to address challenges related to employee engagement, workplace culture, and talent development.
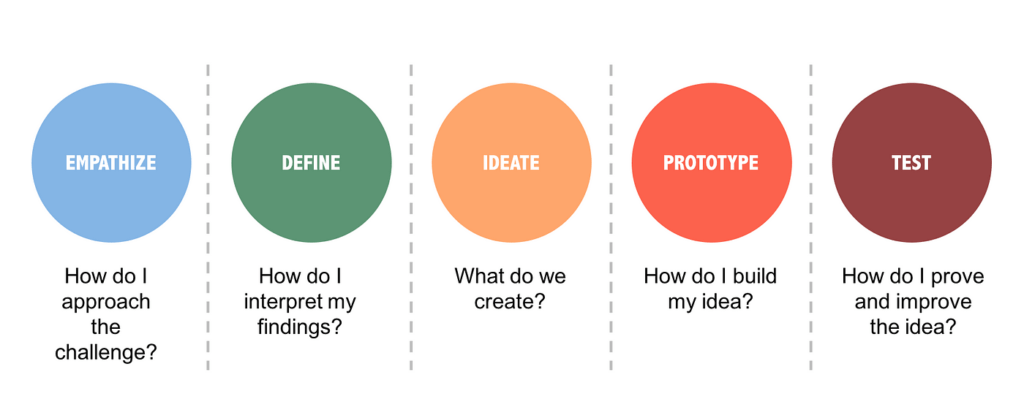
Scenario: Employee Engagement Initiatives
Application: The HR department employs Design Thinking to enhance employee engagement. By empathizing with employees, ideating creative solutions, and prototyping new initiatives, the HR team develops innovative programs fostering a positive workplace culture and increasing employee satisfaction.
Agile Project Management: Flexibility and Collaboration in HR
Agile project management is an iterative, flexible approach that prioritizes collaboration and responsiveness to change. Agile methodologies, such as Scrum, find applications in various industries, including HR.
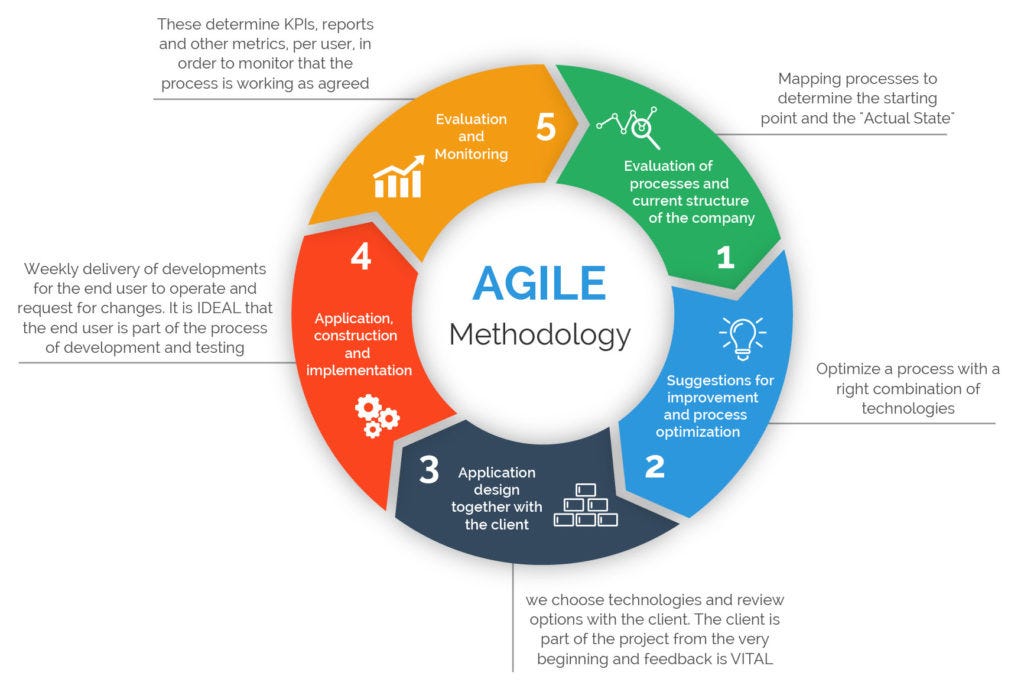
Scenario: Adaptive Performance Management
Application: An HR team adopts Agile methodologies for performance management. Instead of annual reviews, the team implements regular, short feedback cycles, allowing employees and managers to adapt quickly to changing circumstances and goals.
DMAIC vs. DMADV Frameworks: Tailoring Six Sigma in HR
DMAIC and DMADV are Six Sigma frameworks with distinct purposes. DMAIC is used for process improvement, while DMADV is applied to design new processes. In HR, DMAIC may be used to optimize existing talent acquisition processes, while DMADV could be employed to design a new employee onboarding system.
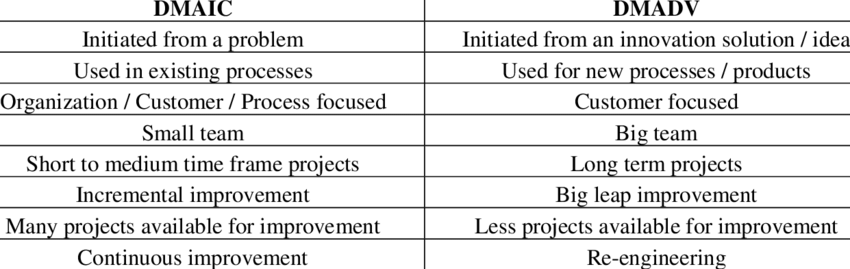
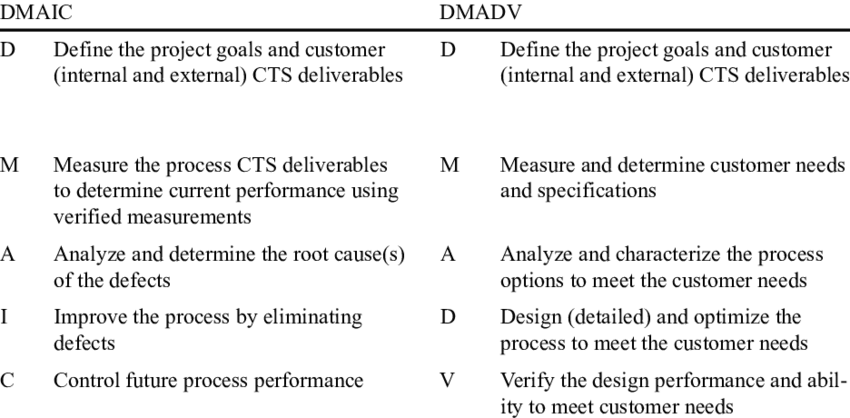
Scenario: Talent Acquisition Optimization vs. New Onboarding System Design
Application: The HR team utilizes DMAIC to improve the efficiency of the recruitment process by defining key metrics, measuring the current process, analyzing bottlenecks, making improvements, and implementing control measures. Simultaneously, DMADV is applied to design a new performance management system from scratch, considering the unique needs and goals of the organization.
Beyond the Basics: DFSS in HR
Design for Six Sigma (DFSS) is an extension of the Six Sigma methodology specifically designed for product or process design. It involves five stages: Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, and Verify. In HR, DFSS can be particularly valuable when creating new HR processes or systems.
Scenario: Designing a Comprehensive Employee Feedback System
Application: The HR team embarks on designing a comprehensive employee feedback system. DFSS is employed, ensuring that the entire process is meticulously defined, measured, analyzed, designed, and verified to meet the specific needs of both employees and the organization.
Frameworks in Innovation, Transformation, Improvement, and New Product Launch Projects
The selection of project management frameworks depends on the nature of the project and organizational goals. Let’s explore scenario-wise applications of different frameworks within HR functions.
- Innovation Projects: Design Thinking and Agile
- Design Thinking fosters a creative and empathetic approach to problem-solving, making it ideal for innovation projects addressing user needs.
- Agile methodologies facilitate rapid development and iteration, ensuring adaptability in response to market changes and customer feedback.
Scenario: Developing Innovative Employee Well-being Programs
Application: The HR team combines Design Thinking to understand and ideate employee well-being programs and Agile methodologies to iteratively develop and adapt these programs based on continuous feedback.
- Transformation Projects: Lean and Six Sigma
- Lean principles streamline processes during organizational transformations, reducing waste and enhancing overall efficiency.
- Six Sigma ensures data-driven improvements, vital for the success and sustainability of transformative initiatives.
Scenario: Restructuring HR Processes for Organizational Transformation
Application: Lean principles are applied to streamline HR processes during organizational restructuring, while Six Sigma is employed to identify and eliminate defects, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of restructured processes.
- Improvement Projects: Six Sigma and Just-in-Time
- Six Sigma provides a structured approach to identify and eliminate defects in existing processes.
- Just-in-Time principles optimize resource utilization and minimize waste in ongoing processes, contributing to continuous improvement.
Scenario: Improving Employee Training Programs
Application: Six Sigma is utilized to analyze and improve existing training processes, ensuring they are defect-free. Simultaneously, Just-in-Time principles are applied to optimize training resource utilization, minimizing unnecessary downtime.
- New Product Launch Projects: Agile and Lean
- Agile methodologies facilitate rapid development and iteration of new products.
- Lean principles minimize waste in the product development process, ensuring efficient resource utilization.
Scenario: Launching a New HR Software Solution
Application: Agile methodologies guide the iterative development of a new HR software solution, allowing the team to respond quickly to changing requirements. Simultaneously, Lean principles are applied to minimize waste in the development process, ensuring efficient use of resources.
Conclusion
Navigating the diverse landscape of project management frameworks requires a nuanced understanding of their principles, methodologies, and applications. Lean, JIT, Six Sigma, Design Thinking, Agile, and DFSS offer organizations a rich toolkit to address challenges within HR functions. By strategically choosing the right framework for each scenario, organizations can optimize processes, enhance efficiency, and foster innovation. The key lies in adaptability, continuous learning, and the ability to tailor these methodologies to the specific needs and goals of the organization. As HR functions continue to evolve, a holistic approach to project management frameworks becomes essential for organizations aiming to stay competitive and responsive to change.











