Project Management Institute’s (PMI) Risk Management Framework is a comprehensive approach that enables organizations to identify, assess, and mitigate potential risks in their projects. While traditionally applied to project management, this framework can also be effectively leveraged by Human Resources (HR) professionals in various scenarios. In this article, we will explore how HR practitioners can utilize the PMI Risk Management Framework to enhance decision-making and strategic planning.
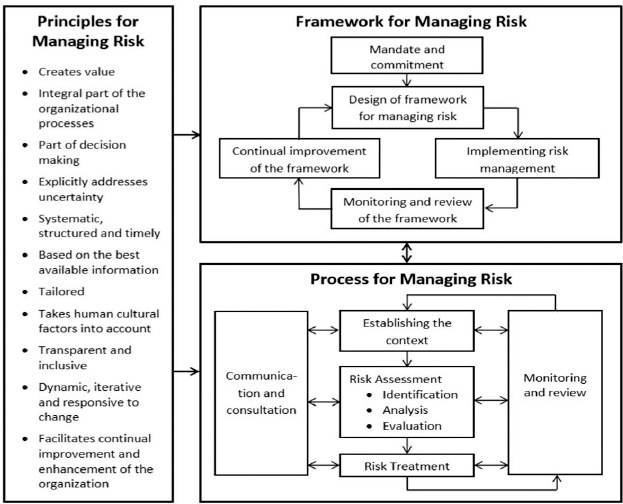
Understanding PMI Risk Management Framework:
PMI’s Risk Management Framework consists of five key processes: Risk Management Planning, Risk Identification, Qualitative Risk Analysis, Quantitative Risk Analysis, and Risk Response Planning. These processes collectively form a structured approach to managing uncertainties and potential obstacles throughout a project lifecycle.
Applying PMI Risk Management Framework in HR:
- Recruitment and Talent Acquisition:
- Risk Management Planning: Define the strategy for recruiting and acquiring talent. Identify potential risks such as skill shortages, competition for talent, and changes in market demand.
- Risk Identification: Identify specific risks related to candidate availability, skill misalignment, or changes in organizational needs.
- Qualitative and Quantitative Risk Analysis: Assess the severity and probability of identified risks. Use quantitative methods to assign numerical values for a more objective evaluation.
- Risk Response Planning: Develop strategies for mitigating identified risks, such as creating a talent pipeline, investing in training programs, or utilizing recruitment agencies.
- Employee Engagement and Retention:
- Risk Management Planning: Formulate plans for maintaining high employee engagement levels. Anticipate potential risks such as burnout, lack of motivation, or inadequate communication.
- Risk Identification: Identify factors that may contribute to decreased employee engagement, such as poor leadership, unclear communication channels, or inadequate recognition.
- Qualitative and Quantitative Risk Analysis: Evaluate the impact and likelihood of risks affecting employee engagement. Use surveys and performance metrics for a quantitative analysis.
- Risk Response Planning: Develop strategies to address identified risks, such as implementing employee wellness programs, enhancing communication channels, or revising performance management processes.
- Succession Planning:
- Risk Management Planning: Develop a comprehensive succession plan to mitigate risks associated with key personnel turnover or unexpected departures.
- Risk Identification: Identify critical positions and potential gaps in the talent pipeline. Recognize risks related to lack of training for potential successors.
- Qualitative and Quantitative Risk Analysis: Assess the impact of losing key personnel and the probability of succession plan failure. Use data to quantify the potential consequences.
- Risk Response Planning: Implement strategies to minimize risks, such as cross-training employees, mentorship programs, and ensuring documentation of critical knowledge.
- Organizational Change Management:
- Risk Management Planning: Plan for effective change management to address potential resistance, productivity decline, or cultural clashes.
- Risk Identification: Identify potential risks associated with changes, including employee resistance, communication breakdowns, and inadequate training.
- Qualitative and Quantitative Risk Analysis: Assess the impact and probability of risks related to organizational change. Utilize surveys and feedback mechanisms for quantitative data.
- Risk Response Planning: Develop strategies to address resistance and potential disruptions, such as targeted communication plans, employee involvement, and training programs.
Conclusion:
Human Resources plays a crucial role in the success of an organization, and by adopting the PMI Risk Management Framework, HR professionals can enhance their decision-making processes, mitigate potential risks, and contribute to the overall strategic goals of the organization. The structured approach provided by the framework enables HR to proactively identify, analyze, and respond to risks in various scenarios, ultimately fostering a more resilient and adaptable workforce.











