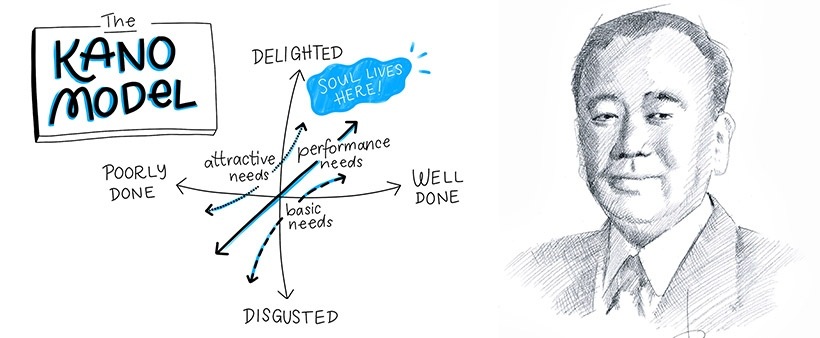
Understanding and improving employee satisfaction is critical for organizational success in the ever-changing landscape of Human Resources (HR). Professor Noriaki Kano’s breakthrough Kano Model transcends existing methodologies by dividing features into various classes depending on their impact on customer satisfaction. In this post, we will look at the Kano Model and how it may transform employee satisfaction initiatives. Real-world examples from prominent firms will demonstrate the revolutionary effect of incorporating the Kano Model into HR processes.
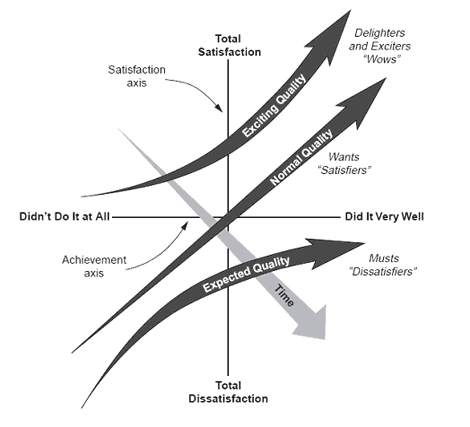
Decoding the Kano Model in HR:
1. Basic Needs (Must-Haves):
- Example: Modern employees consider competitive salaries, job security, and a safe working environment as basic needs. Companies like Google, renowned for its employee-centric approach, ensure robust compensation packages and prioritize workplace safety to meet these fundamental expectations.
2. Performance Needs (Linear Proportional):
- Example: Career development opportunities, flexible work hours, and comprehensive health benefits fall into the category of performance needs. Microsoft, through its “MyMicrosoft” program, provides employees with diverse growth paths and benefits, directly impacting overall satisfaction.
3. Excitement Needs (Delighters or Satisfiers):
- Example: Innovative perks and unique employee engagement initiatives belong to this category. Atlassian, a software company, offers “ShipIt Days,” allowing employees to work on passion projects, fostering a culture of creativity and excitement.
4. Indifferent Needs:
- Example: Mundane aspects like standard office furniture or basic technology fall into the indifferent category. While these factors may not actively contribute to satisfaction, neglecting them could create dissatisfaction over time. Companies like IBM ensure that the workplace environment, while standard, remains comfortable and functional.
5. Reverse Needs (Dissatisfiers):
- Example: Poor communication channels, lack of transparency, and ineffective performance reviews fall into the realm of dissatisfiers. Tesla, recognizing the negative impact of communication gaps, maintains a transparent dialogue with employees, mitigating potential dissatisfaction.
Application of Kano Model in HR:
1. Employee Onboarding:
- During onboarding, basic needs include seamless paperwork and a smooth integration process. Performance needs involve a well-structured orientation program, while excitement needs could encompass personalized welcome kits or mentorship programs.
2. Training and Development:
- Basic needs include access to necessary training materials, while performance needs revolve around personalized development plans. Excitement needs might involve innovative learning platforms or specialized workshops.
3. Workplace Environment:
- Basic needs include a comfortable workspace, performance needs focus on ergonomic enhancements, and excitement needs could involve unique recreational spaces or wellness programs.
4. Communication Channels:
- Basic needs encompass regular updates and accessible communication channels. Performance needs involve interactive forums for feedback, while excitement needs could include innovative platforms for idea-sharing and collaboration.
Conclusion:
In the realm of HR, where employee satisfaction is a cornerstone of organizational success, the Kano Model emerges as a guiding light. By categorizing employee needs into basic, performance, excitement, indifferent, and reverse categories, HR professionals gain a nuanced understanding of what truly drives satisfaction. Real-life examples from leading companies demonstrate the transformative impact of aligning HR practices with the principles of the Kano Model.
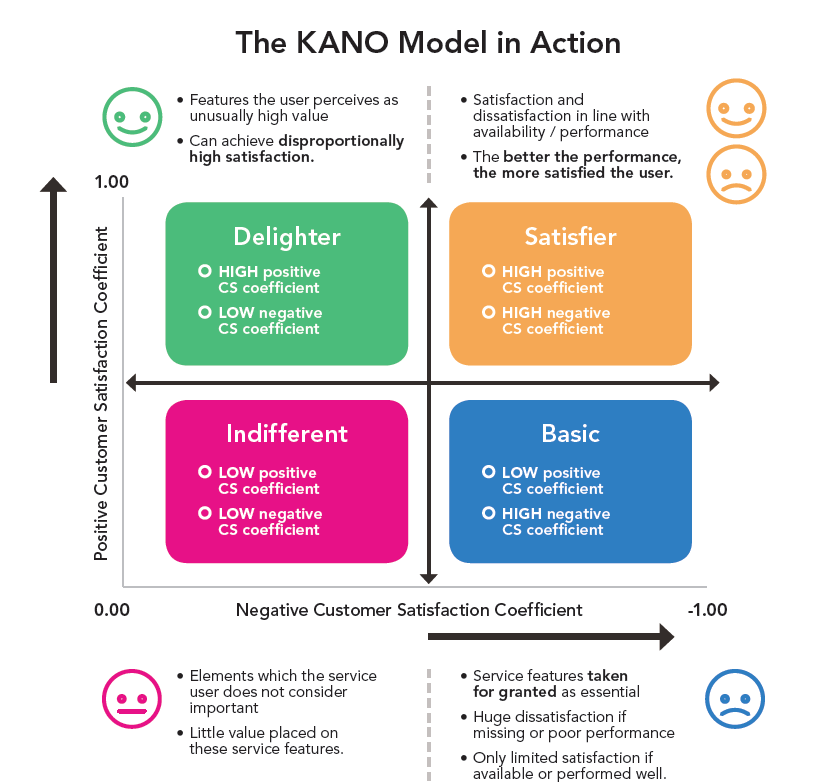
As organizations navigate the complexities of talent management, the Kano Model serves as a strategic tool for prioritizing efforts and resources. By recognizing and addressing basic needs, elevating performance expectations, incorporating excitement factors, managing indifferent elements, and mitigating dissatisfiers, HR leaders can create an environment where employee satisfaction thrives. In the pursuit of organizational excellence, integrating the principles of the Kano Model into HR practices is not merely a strategy; it is a commitment to understanding, valuing, and optimizing the employee experience.