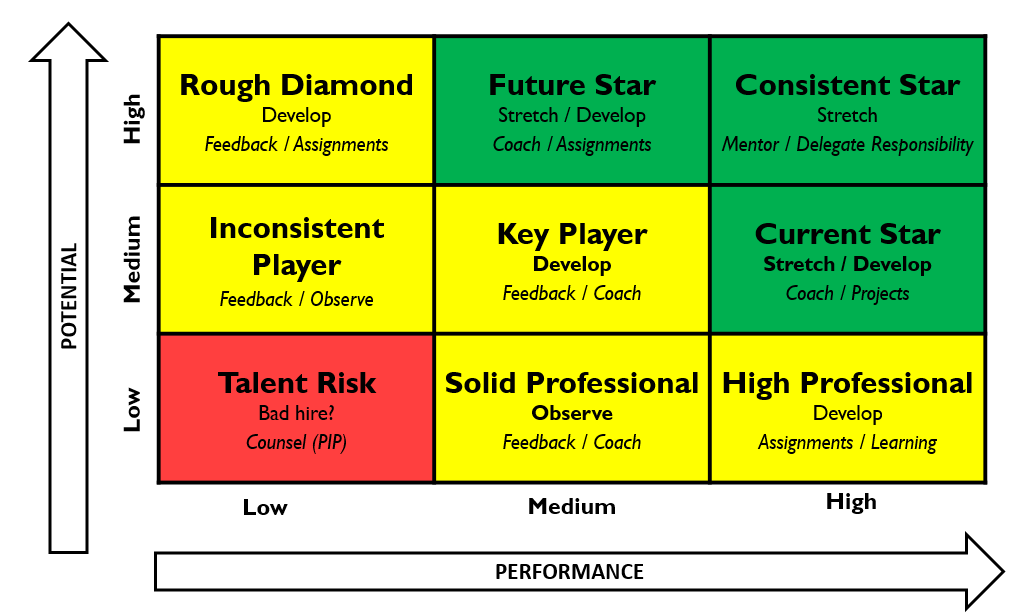
In the dynamic landscape of talent management, strategic tools that aid in identifying and developing high-potential employees are essential for organizational success. General Electric (GE), a global conglomerate, introduced the 9-Box Grid Framework, a seminal tool for talent assessment. This framework has not only become a hallmark of GE’s human resources strategy but has also inspired other organizations to adopt similar approaches to align their workforce with strategic objectives.
Understanding the 9-Box Grid Framework
The 9-Box Grid Framework is a matrix that classifies employees based on their performance and potential. Originating from GE’s practice, this matrix is divided into three performance categories (low, medium, and high) and three potential categories (low, medium, and high), resulting in a 3×3 grid. Each intersection represents a specific segment of the employee population, providing a comprehensive overview of the talent within an organization.
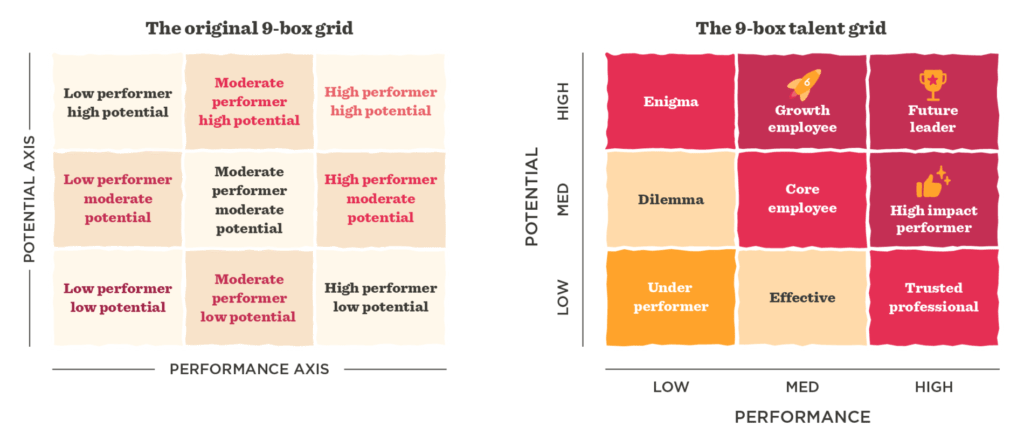
Original 9-Box Grid:
- Historical Context:
- The “original” 9-Box Grid is typically associated with General Electric (GE), where it gained prominence as a talent management tool. Developed in the 1970s, it has a historical significance as one of the earliest talent assessment frameworks.
- Performance and Potential:
- In the original 9-Box Grid, employees are evaluated based on two key factors: their current performance and their potential for future growth and advancement within the organization.
- Succession Planning:
- Originally designed for succession planning, the grid helps identify high-potential individuals who can be groomed for leadership positions, ensuring a continuous pipeline of capable leaders.
9-Box Talent Grid:
- Modern Adaptations:
- The term “9-Box Talent Grid” may be used to signify a modernized or adapted version of the original framework. Organizations might introduce modifications to align with contemporary talent management practices.
- Incorporation of Competencies:
- Some variations of the 9-Box Talent Grid include the consideration of specific competencies or skills, providing a more detailed assessment of an employee’s capabilities beyond the original performance and potential criteria.
- Flexibility and Customization:
- The “talent” aspect in the term might emphasize a broader view of talent, suggesting a more flexible and customizable approach to assessing and developing individuals within an organization.
Key Similarities:
- Matrix Structure:
- Both the original 9-Box Grid and the 9-Box Talent Grid maintain a matrix structure, dividing employees into categories based on their performance and potential.
- Talent Identification:
- The primary purpose of both frameworks is to identify and categorize employees, particularly high-potential individuals, to inform talent management strategies, succession planning, and development programs.
- Strategic Workforce Planning:
- Both models aim to align the organization’s workforce with strategic goals, ensuring that the talent composition supports long-term objectives.
Components of 9 box grid:
Performance Categories:
- High Performers (Top Row): Employees who consistently exceed performance expectations.
- Medium Performers (Middle Row): Employees who meet performance expectations.
- Low Performers (Bottom Row): Employees who struggle to meet performance expectations.
Potential Categories:
- High Potential (Right Column): Employees who show promise and potential for growth and advancement.
- Medium Potential (Middle Column): Employees with moderate growth potential.
- Low Potential (Left Column): Employees with limited growth potential.

Application of the 9-Box Grid Framework
- Talent Identification: The 9-Box Grid helps organizations identify high-potential individuals who can contribute significantly to the company’s future success. This identification facilitates targeted development programs to nurture and retain top talent.
- Succession Planning: By assessing both performance and potential, organizations can create a roadmap for succession planning. High-performing, high-potential employees can be groomed for leadership roles, ensuring a smooth transition when key positions become vacant.
- Performance Management: The framework aids in making informed decisions about performance improvement plans, training initiatives, and talent realignment. Managers can tailor their approach based on an individual’s current performance and potential for growth.
- Strategic Workforce Planning: Aligning the 9-Box Grid with strategic business goals allows organizations to ensure that their workforce composition supports long-term objectives. It enables a proactive approach to workforce planning, anticipating future talent needs rather than reacting to immediate requirements.
- Employee Development: Employees falling into the high-potential category with moderate current performance can be targeted for specific development programs. This ensures that they are equipped with the skills and knowledge needed to excel in future roles.
Challenges and Considerations
While the 9-Box Grid Framework is a powerful tool, its effectiveness depends on accurate and unbiased assessments. Challenges may arise if the criteria for performance and potential are not clearly defined or if there is a lack of objectivity in the evaluation process. Additionally, the framework should be dynamic and regularly reviewed to reflect changes in individual performance and potential.
Pros and Cons of the 9-Box Grid in Talent Management
Pros:
- Clear Visualization:
- Pro: The 9-Box Grid provides a clear visual representation of both an individual’s current performance and potential, aiding in straightforward talent assessment.
- Talent Identification:
- Pro: It excels at identifying high-potential individuals, allowing organizations to nurture and invest in the future leaders of the company.
- Succession Planning:
- Pro: Enables effective succession planning by identifying and grooming high-performing, high-potential employees for leadership roles.
- Strategic Workforce Planning:
- Pro: Aligning the grid with strategic goals helps organizations ensure that their workforce composition supports long-term objectives.
- Objective Decision-Making:
- Pro: Provides a structured approach to decision-making, reducing biases and subjectivity in talent assessment.
Cons:
- Simplification of Talent:
- Con: The 9-Box Grid may oversimplify talent by reducing it to a two-dimensional representation, potentially neglecting nuanced skills and qualities.
- Static Nature:
- Con: The framework can be static, potentially missing real-time changes in an employee’s performance or potential.
- Potential for Bias:
- Con: Without careful calibration, there is a risk of bias in assessments, leading to inaccurate placement of individuals on the grid.
- Inadequate Nuances:
- Con: The grid may not capture the full spectrum of employee nuances, such as specialized skills or contributions to team dynamics.
Other Models and Frameworks:
- Balanced Scorecard:
- Outweighs Cons: The Balanced Scorecard considers financial, customer, internal process, and learning and growth perspectives, providing a more comprehensive view of organizational performance.
- Nine-Box Matrix with Competencies:
- Outweighs Cons: By incorporating specific competencies into the grid, organizations can address the oversimplification concern, offering a more detailed evaluation.
- 360-Degree Feedback:
- Outweighs Cons: Gathering feedback from multiple sources provides a holistic understanding of an employee’s performance and potential, mitigating biases.
Integration with Other Models:
- Holistic Talent Management:
- The 9-Box Grid can be used in conjunction with other models, such as the Balanced Scorecard and 360-Degree Feedback, to create a more holistic talent management approach.
- Customization:
- Organizations can tailor the 9-Box Grid to incorporate specific competencies or performance metrics from other models, ensuring a more customized and nuanced assessment.
Step-wise Implementation for Talent Management and Succession Planning:
- Define Criteria:
- Clearly define the criteria for performance and potential, ensuring alignment with organizational goals.
- Training and Calibration:
- Train assessors to ensure consistency and minimize biases. Regular calibration sessions can help fine-tune evaluations.
- Customization:
- Customize the 9-Box Grid to include competencies or metrics relevant to the organization’s unique needs.
- Integration with Other Models:
- Explore ways to integrate the 9-Box Grid with other models, fostering a comprehensive approach to talent management.
- Regular Review and Update:
- Periodically review and update the grid to reflect changes in employee performance and potential, maintaining its relevance.
- Feedback Mechanism:
- Implement a robust feedback mechanism, incorporating inputs from multiple sources for a more comprehensive talent assessment.
- Continuous Improvement:
- Foster a culture of continuous improvement, allowing the talent management system to evolve based on organizational needs and industry trends.
By carefully considering the pros and cons, integrating with other models, and following a step-wise implementation approach, organizations can leverage the 9-Box Grid effectively for talent management and succession planning, ensuring a well-rounded and forward-thinking workforce.
Industry Insights: Companies Embracing Similar Frameworks
- Microsoft’s Nine-Box Performance and Potential Matrix: Microsoft, a technology giant, has adopted a nine-box matrix similar to GE’s for talent assessment. By evaluating both performance and potential, Microsoft identifies individuals who not only excel in their current roles but also have the capability to take on higher responsibilities in the future.
- Procter & Gamble’s Talent Marketplace: Procter & Gamble (P&G) utilizes a talent marketplace model, akin to the principles of the 9-Box Grid, to identify and develop high-potential employees. This model emphasizes cross-functional experiences, allowing employees to showcase their potential for growth in various roles within the organization.
- Coca-Cola’s Leadership Pipeline Assessment: Coca-Cola employs a leadership pipeline assessment that considers both current performance and future potential. By doing so, the company ensures a steady flow of talent into leadership positions, aligning its workforce with the strategic goals of the organization.
Conclusion
General Electric’s 9-Box Grid Framework remains a cornerstone in the field of talent management. By providing a structured approach to evaluating employees based on both performance and potential, organizations can make strategic decisions that foster growth, innovation, and success. As businesses evolve, the 9-Box Grid continues to be a valuable tool for aligning talent with organizational objectives and ensuring a resilient and forward-thinking workforce.