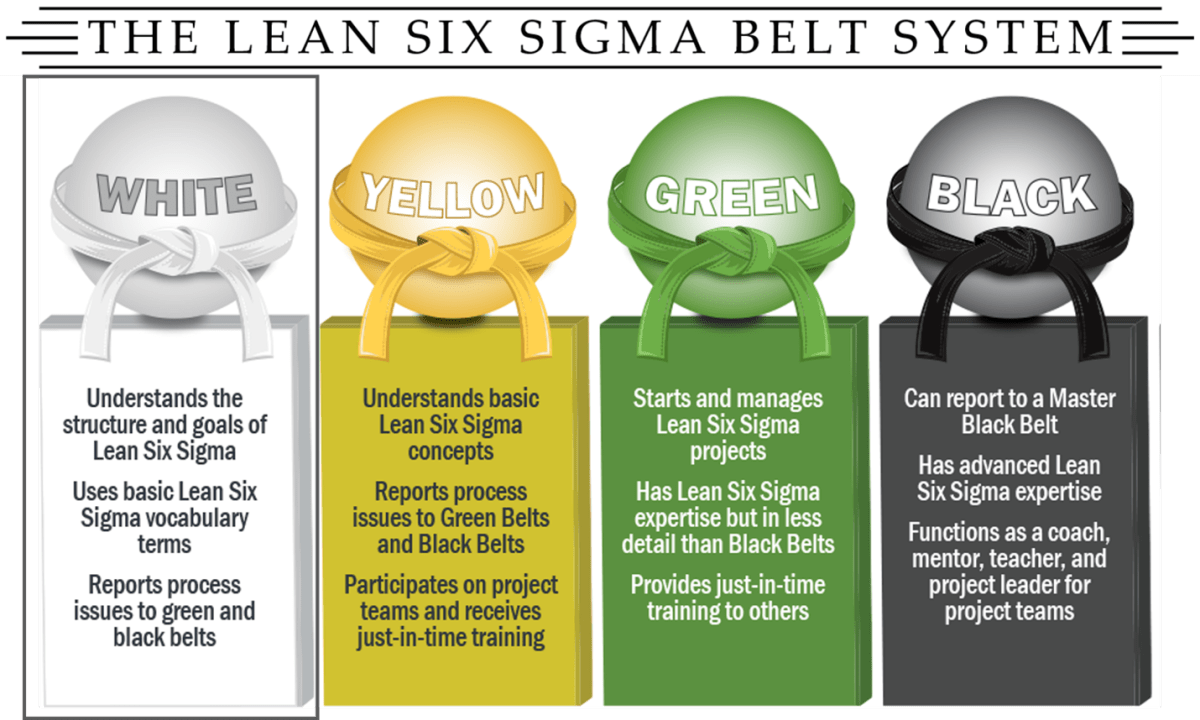
In the fast-paced world of business, organizations are constantly on the lookout for innovative ways to enhance efficiency, cut costs, and maximize productivity. While Lean Six Sigma methodologies have traditionally found their home in manufacturing and operations, their application has evolved to address challenges in areas that were once considered unconventional, such as Human Resources (HR). This article explores the transformative impact of Lean Six Sigma Black Belt in HR problem-solving, elucidating its relevance, real-world applications, and the step-by-step journey through the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) framework.
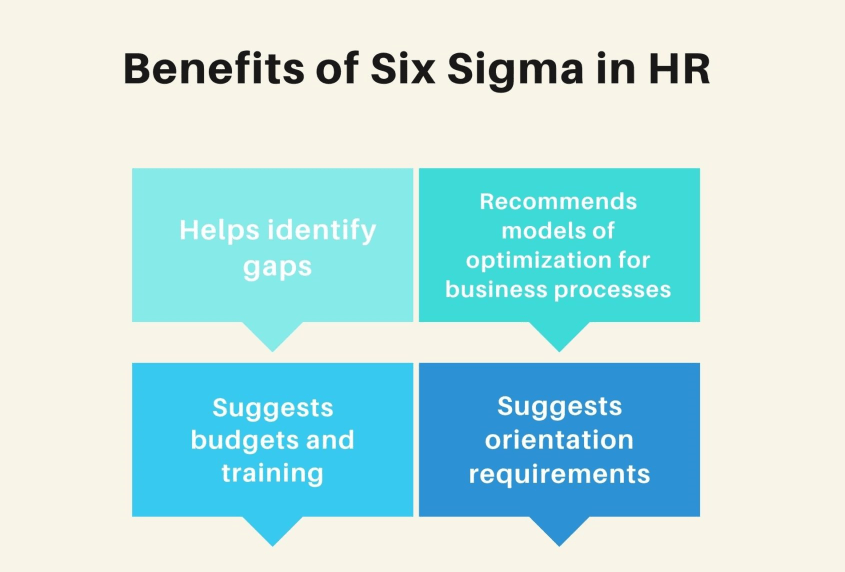
The Marriage of Lean Six Sigma and HR:
In recent years, forward-thinking companies have recognized the potential of Lean Six Sigma in HR processes. The Lean Six Sigma Black Belt, a certified professional trained in advanced problem-solving techniques, plays a pivotal role in this integration. One such company that successfully implemented Lean Six Sigma in HR is General Electric (GE).
Case Study: General Electric
General Electric, a multinational conglomerate, faced challenges in its HR processes, leading to increased operational costs and a decline in employee satisfaction. By employing Lean Six Sigma Black Belts, GE initiated a transformative journey to streamline HR operations and improve overall organizational efficiency.
DMAIC Framework:
1. Define:
In the Define phase, the focus is on understanding the problem and setting clear project objectives. The Lean Six Sigma Black Belt collaborates with HR professionals to identify the pain points and establish a project charter. This phase sets the foundation for the entire improvement process.
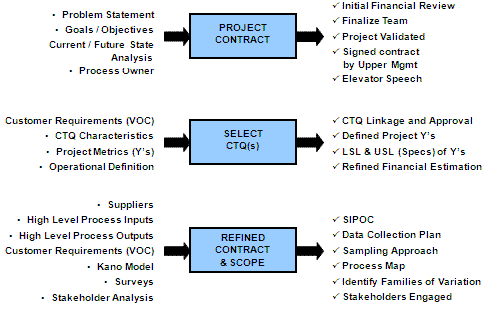
Example: At GE, the Define phase involved identifying specific HR processes causing delays and dissatisfaction among employees. The project charter outlined objectives such as reducing turnaround time for employee onboarding and enhancing the accuracy of performance appraisals.
2. Measure:
Once the problem is defined, the Measure phase involves collecting relevant data to quantify the extent of the issue. Lean Six Sigma Black Belts employ statistical tools to analyze existing HR processes and identify areas that require improvement.
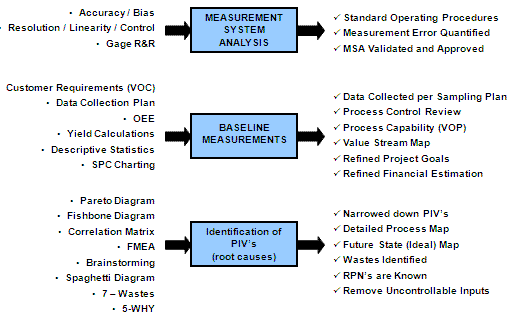
Example: GE utilized key performance indicators (KPIs) such as onboarding duration, error rates in documentation, and employee feedback scores to measure the efficiency and effectiveness of HR processes. This data-driven approach provided a clear understanding of the magnitude of the problem.
3. Analyze:
In the Analyze phase, the Lean Six Sigma team delves deeper into the data to identify root causes of the problem. Various analytical tools, such as Fishbone diagrams and Pareto charts, aid in pinpointing the factors contributing to inefficiencies in HR processes.
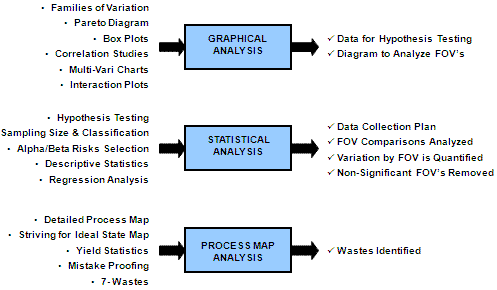
Example: At GE, the Analyze phase revealed that communication gaps between HR and other departments, coupled with manual data entry errors, were the primary causes of delays in onboarding. This insight directed the focus towards targeted solutions.
4. Improve:
Armed with a comprehensive understanding of the problem, the Lean Six Sigma team moves on to the Improve phase, where they brainstorm and implement solutions. The emphasis is on optimizing HR processes to eliminate root causes and enhance overall efficiency.
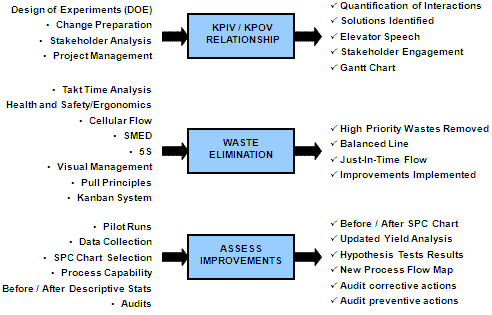
Example: GE introduced automation in the onboarding process and implemented a centralized communication system to bridge gaps between departments. Additionally, employee training programs were revamped to reduce errors in performance appraisals. These improvements led to a significant reduction in onboarding time and enhanced accuracy in evaluations.
5. Control:
The Control phase ensures that the improvements are sustained over the long term. Lean Six Sigma Black Belts work closely with HR teams to develop control plans, monitor performance, and implement preventive measures to prevent the recurrence of issues.
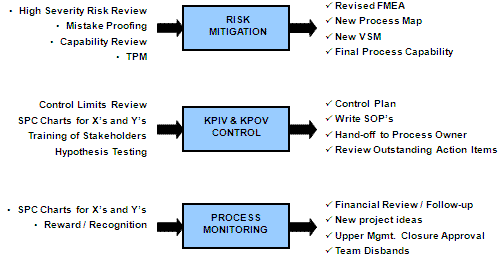
Example: At GE, control mechanisms involved regular audits of HR processes, continuous training for HR staff, and feedback loops from employees. This proactive approach helped to maintain the efficiency gains achieved during the improvement phase.
Tools Used in Lean Six Sigma for HR:
- Process Mapping:
- Purpose: Visualize and understand HR processes.
- Example: Mapping the employee onboarding process at GE highlighted bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
- Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa):
- Purpose: Identify root causes of HR problems.
- Example: At GE, the Fishbone diagram revealed that poor communication and manual errors were major contributors to delays in HR processes.
- Pareto Chart:
- Purpose: Prioritize HR issues based on their impact.
- Example: GE used a Pareto chart to identify the most critical factors affecting HR efficiency, allowing them to prioritize improvement efforts.
- Statistical Analysis:
- Purpose: Analyze quantitative data to understand trends and patterns.
- Example: Statistical analysis at GE identified correlations between communication gaps and onboarding delays, providing a basis for targeted improvements.
- Control Charts:
- Purpose: Monitor ongoing HR process performance.
- Example: GE implemented control charts to track onboarding duration, ensuring that any deviations from the established norms were promptly addressed.
Scenarios in which Lean Six Sigma Black Belt is Beneficial in HR:
- Talent Acquisition and Onboarding:
- Scenario: Excessive delays in the recruitment process leading to a loss of top talent.
- Solution: Lean Six Sigma methodologies can be applied to streamline the hiring process, reduce time-to-fill metrics, and enhance the onboarding experience.
- Performance Management:
- Scenario: Inaccurate performance appraisals affecting employee morale.
- Solution: Lean Six Sigma Black Belts can identify and eliminate errors in performance management processes, ensuring fair and accurate evaluations.
- Employee Engagement:
- Scenario: Low employee satisfaction and engagement levels.
- Solution: Lean Six Sigma can be applied to analyze factors contributing to low engagement, leading to targeted interventions for improvement.
- Training and Development:
- Scenario: Ineffective training programs leading to skill gaps.
- Solution: Lean Six Sigma methodologies can optimize training processes, ensuring that they align with organizational goals and result in improved employee competency.
Conclusion:
The marriage of Lean Six Sigma Black Belt methodologies with HR processes is a powerful alliance that promises transformative results for organizations. By applying the DMAIC framework and leveraging various tools, companies can not only address existing HR challenges but also foster a culture of continuous improvement. Real-world examples, such as General Electric, demonstrate that the application of Lean Six Sigma in HR is not just a theoretical concept but a pragmatic and effective approach to enhance organizational efficiency and employee satisfaction. As businesses continue to evolve, the integration of Lean Six Sigma Black Belt in HR problem-solving stands as a beacon of innovation, guiding companies towards a future where people processes are as optimized as their operational counterparts.