Imagine a workplace where the air is charged with positivity, employees are motivated, and innovation flows seamlessly through the corridors. This utopian vision is not merely a flight of fancy but a tangible reality for organizations that have embraced the transformative power of Appreciative Inquiry (AI) in their Human Resources (HR) practices. In a world often fixated on identifying and rectifying weaknesses, AI stands as a beacon, spotlighting the strengths, successes, and untapped potential within an organization. As we embark on a journey to explore the depth of Appreciative Inquiry in the HR domain, let’s delve into real-world scenarios where this methodology has not only initiated change but has become the catalyst for a cultural revolution.
Appreciative Inquiry: A Comprehensive Exploration
Understanding Appreciative Inquiry:
At its core, Appreciative Inquiry is a collaborative and strengths-based approach to organizational development that seeks to identify and build upon what is already working well within an organization. Developed in the 1980s by David Cooperrider and Suresh Srivastva, AI represents a departure from traditional problem-solving methods. Instead of dwelling on weaknesses and challenges, AI encourages organizations to leverage their existing strengths to drive positive change.
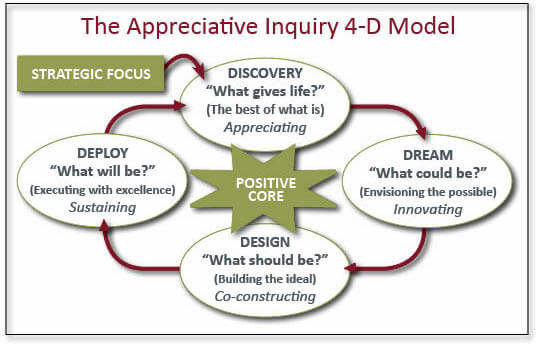
The 4-D Cycle of Appreciative Inquiry:
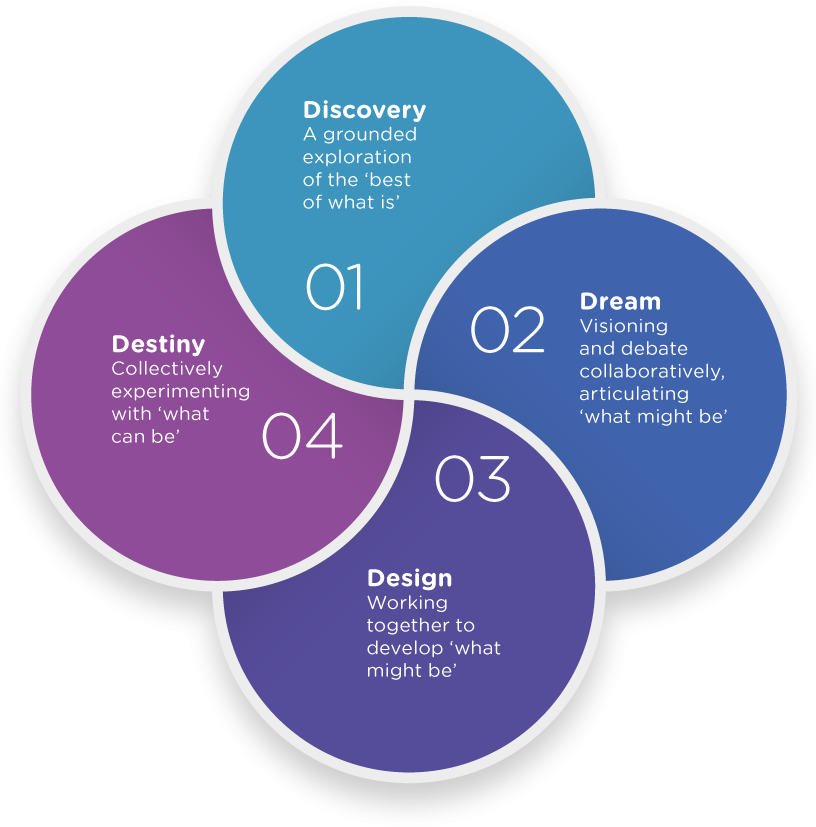
- Discovery: Unearthing the Gems Within
The first phase, Discovery, involves identifying the positive aspects and strengths within an organization. It encourages employees to share stories of success, high points, and moments when they felt most engaged. This phase sets the stage for a positive dialogue, uncovering the hidden gems that often go unnoticed in the day-to-day hustle.
- Dream: Envisioning Tomorrow’s Success
In the Dream phase, organizations collectively envision their ideal future based on the positive elements identified in the Discovery phase. It is a process of collectively dreaming about what the organization could become. This phase taps into the creative potential of employees, encouraging them to imagine a future where their strengths are maximized.
- Design: Strategies for Success
Building on the dreams and positive aspects, the Design phase involves developing practical strategies and plans to achieve the envisioned future. It is a collaborative effort that engages employees at various levels to contribute to the design of initiatives. Here, the dreams take tangible form as organizations map out the steps to turn their positive vision into reality.
- Destiny (or Deployment): Making Dreams Reality
This final phase, Destiny (or Deployment), involves implementing the designed initiatives and continually assessing and adapting them based on feedback. It is an ongoing process that fosters a culture of continuous improvement. In this phase, organizations witness the manifestation of their dreams, as the designed strategies are put into action, bringing about tangible and positive change.
Real-World Examples:
Scenario 1: British Airways Takes Flight Towards Positivity
In the not-so-distant past, British Airways found itself navigating turbulent skies. Financial challenges were compounded by a disengaged workforce, threatening the very essence of the airline. Enter Appreciative Inquiry. The organization initiated the Discovery phase by encouraging employees to share stories of success, high points, and moments of exceptional service. By focusing on the positive experiences within the company, British Airways set the stage for a cultural transformation.
During the Dream phase, employees collectively envisioned an ideal future where teamwork, innovation, and a customer-centric approach prevailed. With these dreams as the guiding light, the Design phase saw the development of practical strategies to bring about the desired changes. The Destiny phase was marked by the implementation of these initiatives, resulting in improved employee morale, enhanced customer service, and significant cost savings.
Scenario 2: McDonald’s Serves Up a Culture of Positivity
The fast-food giant McDonald’s, known for its golden arches and iconic menu, recognized the need for a cultural facelift. In a bid to strengthen its corporate culture and boost employee engagement, the company turned to Appreciative Inquiry. Through the Discovery phase, McDonald’s unearthed success stories and positive elements within its operations. Employees reminisced about instances where teamwork triumphed and customer experiences were exemplary.
The Dream phase allowed the company to collectively imagine an ideal workplace based on these positive aspects. Subsequently, the Design phase saw the formulation of strategies to enhance employee satisfaction and create a more positive work environment. As these initiatives were deployed in the Destiny phase, McDonald’s witnessed a positive shift in its workplace culture, showcasing the tangible benefits of Appreciative Inquiry.
Scenario 3: Johnson & Johnson’s Prescription for Team Harmony
In the competitive landscape of the pharmaceutical industry, Johnson & Johnson recognized the critical role of teamwork and collaboration in driving success. Appreciative Inquiry became the prescription for fostering a positive team environment. The Discovery phase brought to light instances of successful team dynamics and positive experiences within the organization.
During the Dream phase, employees collectively envisioned a workplace where collaboration thrived and individual strengths complemented each other. Strategies were then designed in the third phase to enhance teamwork, and in the Destiny phase, these initiatives were put into action. The result? A more cohesive and supportive work environment that mirrored the positive vision crafted during the Appreciative Inquiry process.
How is Appreciative Inquiry different from Traditional Problem Solving Approaches:
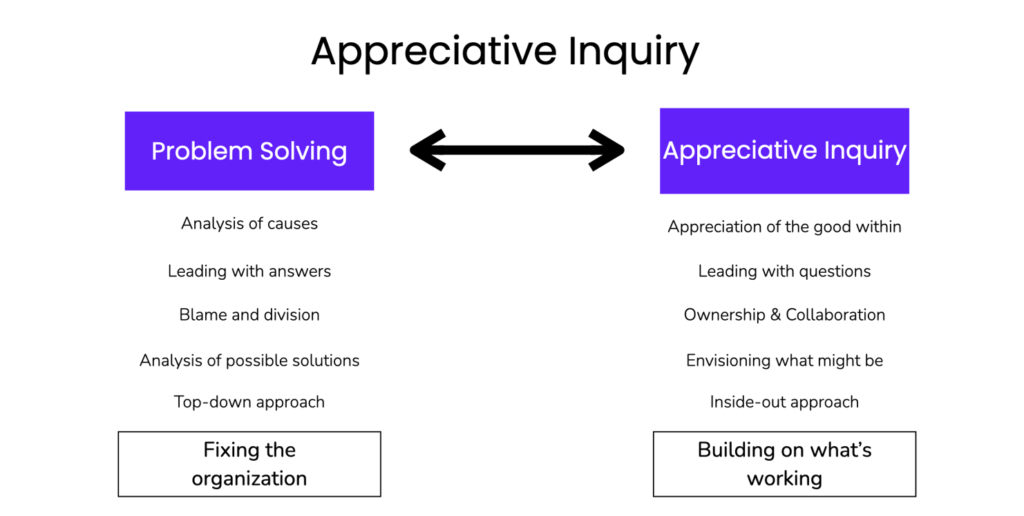
Appreciative Inquiry (AI) stands in stark contrast to traditional problem-solving approaches by shifting the focus from weaknesses and challenges to strengths and opportunities within an organization. Unlike conventional methods that often center on identifying and rectifying problems, AI encourages a positive and constructive outlook. Rather than dwelling on what is not working, AI initiates a discovery process to unearth success stories, positive experiences, and existing strengths. This shift in perspective not only fosters a more optimistic organizational culture but also promotes collaboration and innovation. Traditional problem-solving tends to be reactive, addressing issues as they arise, while AI is proactive, envisioning an ideal future and designing strategies to achieve it. By concentrating on what is working well, Appreciative Inquiry creates a foundation for sustainable positive change, engaging employees in a collective effort to shape a more inspiring and successful organizational landscape.
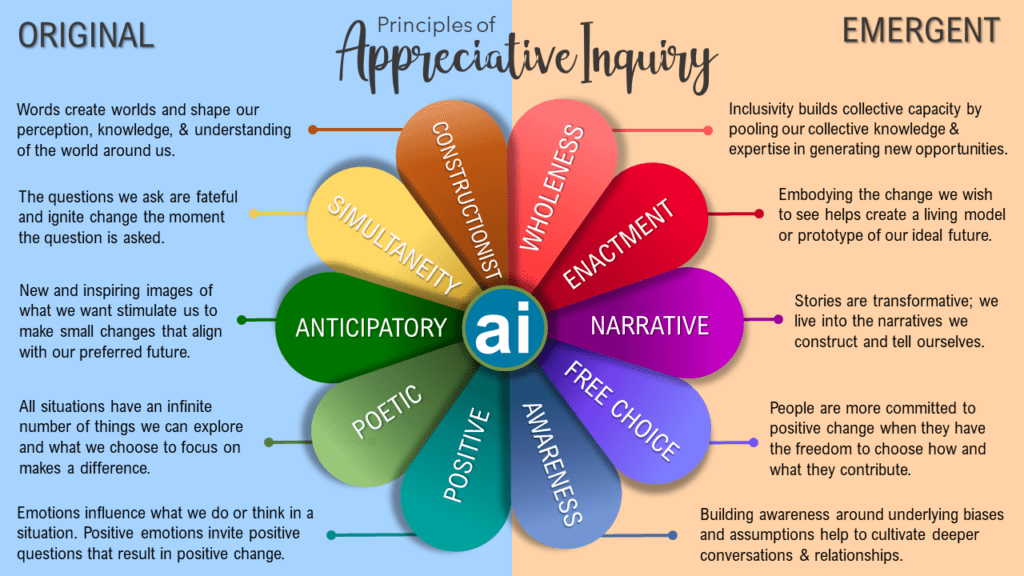
Foundational Principles of Appreciative Inquiry: Shaping Positive Organizational Change
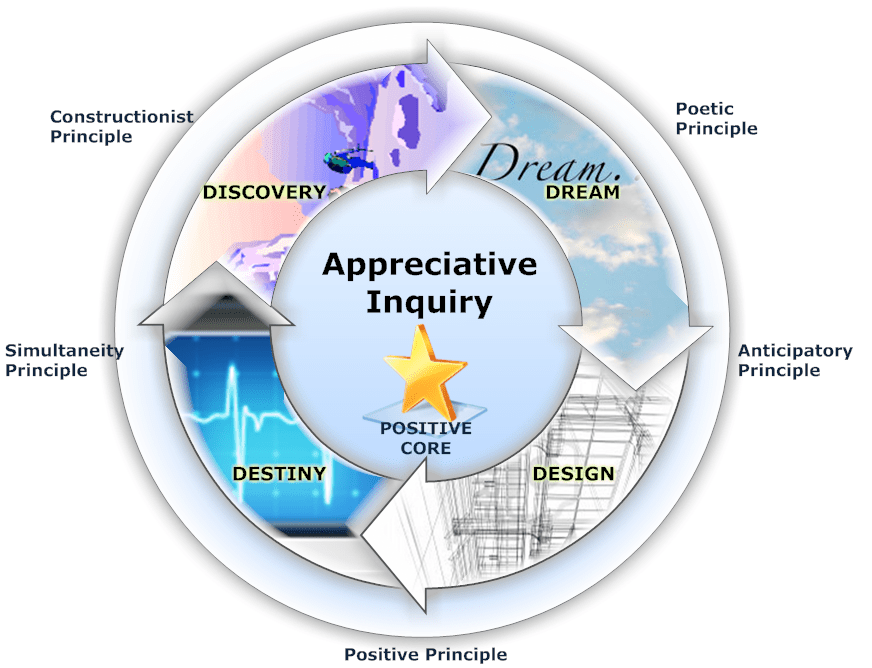
In the context of Appreciative Inquiry (AI), these principles form the foundation of the methodology and guide the mindset and actions of those involved. Let’s explore each principle in the context of AI:
- Poetic Principle:
- Meaning: The poetic principle emphasizes the idea that organizations and their futures are open to interpretation and can be shaped through the stories and language used to describe them.
- Implication: It encourages individuals to view organizations as dynamic, evolving narratives, and through positive and constructive storytelling, participants can influence the collective understanding of the organization.
- Constructionist Principle:
- Meaning: The constructionist principle suggests that our understanding of reality is socially constructed through language and communication. It emphasizes the idea that the way we talk about things influences our perception of them.
- Implication: In AI, this principle encourages participants to engage in positive and generative conversations. By constructing a positive narrative, individuals can contribute to the co-creation of a more positive organizational reality.
- Simultaneity Principle:
- Meaning: The simultaneity principle asserts that change is not a linear process but can happen in the present moment. It suggests that inquiry and change are simultaneous rather than sequential.
- Implication: In AI, this principle encourages participants to engage in positive dialogue and action in the present. It emphasizes the idea that positive change can occur as individuals inquire into and appreciate the positive aspects of their organization.
- Anticipatory Principle:
- Meaning: The anticipatory principle posits that images of the future guide and influence human behavior in the present. It emphasizes the idea that what we anticipate influences our actions.
- Implication: In AI, this principle encourages participants to envision a positive future. By collectively dreaming and articulating a positive vision, individuals can influence their present actions to align with the desired future state.
- Positive Principle:
- Meaning: The positive principle underscores the idea that focusing on what works well and what is positive within an organization generates more positive energy and outcomes than focusing on problems and deficits.
- Implication: In AI, this principle guides the inquiry process to seek out and amplify the positive aspects of an organization. It suggests that by appreciating and building upon strengths, individuals can create a more positive and generative organizational culture.
These principles collectively form the philosophical underpinnings of Appreciative Inquiry, guiding practitioners to approach organizational development with a positive and strengths-based perspective. By embracing these principles, individuals can foster a culture of collaboration, innovation, and continuous positive change within their organizations.
Significance in HR Domain:
Appreciative Inquiry’s significance in the HR domain extends far beyond being a mere organizational development tool; it represents a paradigm shift in how HR professionals approach their roles and responsibilities.
- Employee Engagement and Well-being: Appreciative Inquiry serves as a catalyst for boosting employee engagement by fostering a workplace culture that recognizes and celebrates individual and collective successes. The emphasis on positive experiences contributes to a more supportive and empowering environment, enhancing overall employee well-being.
- Organizational Culture Transformation: Traditional HR methods often focus on problem areas, which may inadvertently contribute to a culture of blame or negativity. AI, on the other hand, facilitates a transformative shift in organizational culture. By concentrating on strengths and positive aspects, it lays the groundwork for a culture of collaboration, innovation, and mutual support.
- Change Management with a Positive Outlook: Change is a constant in the business world, and AI provides HR professionals with a positive framework for managing change. Engaging employees in the AI process from the beginning makes them stakeholders in the change initiatives, reducing resistance and fostering a sense of ownership in the transformation journey.
- Innovative HR Strategies: Appreciative Inquiry inspires HR professionals to think innovatively about their strategies. By tapping into the collective wisdom of employees and focusing on what works well, HR can develop initiatives that not only address challenges but also capitalize on the organization’s strengths, driving continuous improvement.
- Talent Retention and Attraction: A positive workplace culture, as nurtured by Appreciative Inquiry, becomes a magnet for talent. Employees are more likely to stay in an organization where their contributions are recognized and where they feel a sense of purpose. In a competitive talent landscape, AI becomes a strategic tool for attracting and retaining top performers.
- Positive Leadership Development: Leadership plays a pivotal role in shaping organizational culture. Appreciative Inquiry promotes positive leadership by encouraging leaders to focus on strengths, foster open communication, and inspire a shared vision. This, in turn, creates a leadership style that motivates and empowers teams.
- Continuous Improvement and Learning: AI is inherently aligned with the concept of continuous improvement. The iterative nature of the 4-D Cycle encourages organizations to consistently reassess and refine their strategies based on feedback and evolving circumstances. This commitment to learning and improvement becomes ingrained in the organizational DNA.
- Enhanced Employee-Centric Approach: Appreciative Inquiry places employees at the center of the change process. Their voices, experiences, and aspirations become integral to shaping the organization’s future. This employee-centric approach not only improves morale but also ensures that HR strategies are aligned with the needs and expectations of the workforce.
In essence, Appreciative Inquiry in the HR domain is a powerful tool for creating a positive, adaptive, and innovative organizational culture. It transforms HR from a reactive problem-solving function to a proactive force that leverages the collective strengths of the workforce to drive sustained success and growth. As HR professionals increasingly recognize the need for holistic and positive approaches, Appreciative Inquiry emerges as a cornerstone in shaping the future of HR practices.
Conclusion:
As we conclude our exploration into the realm of Appreciative Inquiry in HR, it becomes evident that this methodology is not just a theoretical concept but a dynamic force driving positive change within organizations. Real-world scenarios of British Airways, McDonald’s, and Johnson & Johnson serve as living testimonials to the transformative power of AI. In a world where the pursuit of success often involves acknowledging and building upon strengths rather than dwelling on weaknesses, Appreciative Inquiry emerges as the compass guiding organizations towards a brighter, more positive future. The journey towards success begins with the recognition that the seeds of triumph are often found in the soil of positivity, collaboration, and the unwavering belief in an organization’s untapped potential.
Thought-Provoking Questions:
As we ponder the impact of Appreciative Inquiry on the landscape of HR, let’s consider some thought-provoking questions. How might organizations across various industries leverage AI to not only navigate challenges but also to thrive in an ever-changing business environment? In what ways can the principles of Appreciative Inquiry be tailored to suit the unique needs of different organizations? And, perhaps most importantly, how can HR professionals inspire a cultural shift within their organizations, moving from a problem-centric approach to one that celebrates successes, fosters collaboration, and unlocks the full spectrum of human potential? As we embark on this journey of exploration, these questions serve as guideposts, prompting us to envision a future where positivity reigns supreme in the world of Human Resources.